Preserved ex vivo inflammatory status in decidual cells from women with preterm labor and subclinical intrauterine infection
- PMID: 22928002
- PMCID: PMC3425489
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043605
Preserved ex vivo inflammatory status in decidual cells from women with preterm labor and subclinical intrauterine infection
Abstract
Objective: To compare the inflammatory response preserved ex vivo by decidual cells isolated from women who experienced preterm labor with and without subclinical intrauterine infection.
Methods: Fetal membranes were obtained after cesarean section from 35 women who delivered before 37 weeks of gestation following spontaneous preterm labor, with no clinical evidence of intrauterine infection. Decidua was microbiologically tested and cultured. Concentrations of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-4, IL-10), pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β and TNF-α), and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-8, MMP-9) were measured in the supernatants using Bio-Plex, and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) was measured by enzyme immunoassay.
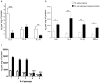
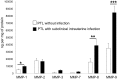
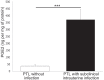
Results: Subclinical infection was confirmed in 10 women (28.5%). Microorganisms isolated were Ureaplasma urealyticum (4), group B streptococci (3), Gardnerella vaginalis (1), and Escherichia coli (2). We found a significant increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a significant decrease of anti-inflammatory cytokines in supernatants from decidual cells obtained from women with preterm labor and subclinical intrauterine infection compared to women without infection. Secretion of MMP-1, MMP-8, MMP-9 and PGE(2) was significantly higher in infected women. Secretion of IL-8 by decidual cells from infected women persisted upon repeated in vitro culture passages.
Conclusions: Almost 30% of idiopathic preterm labor cases were associated with subclinical intrauterine infection, and decidual cells isolated from these cases preserved an ex vivo inflammatory status after in vivo bacterial exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Preterm birth: Causes, consequences, and prevention. Brief report by The Institute of Medicine of the National Academies (2006). Available: http://www.iom.edu/Reports/2006/Preterm-Birth-Causes-Consequences-and-Pr....
-
- Goncalves LF, Chaiworapongsa T, Romero R (2002) Intrauterine infection and prematurity. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 8: 3–13. - PubMed
-
- Klein LL, Gibbs RS (2005) Infection and preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 32: 397–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

