Evaluation of the Effects of Sativex (THC BDS: CBD BDS) on Inhibition of Spasticity in a Chronic Relapsing Experimental Allergic Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Model of Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 22928118
- PMCID: PMC3423911
- DOI: 10.5402/2012/802649
Evaluation of the Effects of Sativex (THC BDS: CBD BDS) on Inhibition of Spasticity in a Chronic Relapsing Experimental Allergic Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Model of Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
This study investigated the antispasticity potential of Sativex in mice. Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis was induced in adult ABH mice resulting in hind limb spasticity development. Vehicle, Sativex, and baclofen (as a positive control) were injected intravenously and the "stiffness" of limbs assessed by the resistance force against hind limb flexion. Vehicle alone caused no significant change in spasticity. Baclofen (5 mg/kg) induced approximately a 40% peak reduction in spasticity. Sativex dose dependently reduced spasticity; 5 mg/kg THC + 5 mg/kg CBD induced approximately a 20% peak reduction; 10 mg/kg THC + 10 mg/kg CBD produced approximately a 40% peak reduction in spasticity. Sativex has the potential to reduce spasticity in an experimental mouse model of multiple sclerosis (MS). Baclofen reduced spasticity and served as a positive control. Sativex (10 mg/kg) was just as effective as baclofen, providing supportive evidence for Sativex use in the treatment of spasticity in MS.
Figures
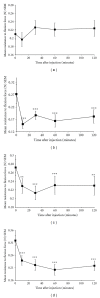
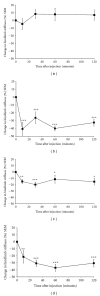
References
-
- Marra GA, D’Aleo G, Di Bella P, Bramanti P. Intrathecal baclofen therapy in patients with severe spasticity. Acta Neurochirurgica, Supplementum . 2007;(97):173–180. - PubMed
-
- Sherwood AM, Graves DE, Priebe MM. Altered motor control and spasticity after spinal cord injury: subjective and objective assessment. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development . 2000;37(1):41–52. - PubMed
-
- Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J. Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment . 2003;7(40):1–111. - PubMed
-
- Pappalardo A, Castiglione A, Restivo DA, Calabrese A, Patti F. Non-pharmacologic interventions for spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis. Neurological Sciences . 2006;27(supplement 4):s316–s319.
-
- Wynn D. Management of physical symptoms. International Journal of MS Care . 2006;13:20–26.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

