Strategies to prevent anthracycline-related congestive heart failure in survivors of childhood cancer
- PMID: 22928146
- PMCID: PMC3426199
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/713294
Strategies to prevent anthracycline-related congestive heart failure in survivors of childhood cancer
Abstract
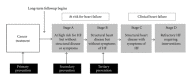
Cardiovascular complications are a leading cause of therapy-related morbidity and mortality in long-term survivors of childhood malignancy. In fact, childhood cancer survivors are at a 15-fold risk of developing CHF compared to age-matched controls. There is a strong dose-dependent association between anthracycline exposure and risk of CHF, and the incidence increases with longer followup. Outcome following diagnosis of CHF is generally poor, with overall survival less than 50% at 5 years. The growing number of childhood cancer survivors makes it imperative that strategies be developed to prevent symptomatic heart disease in this vulnerable population. We present here an overview of the current state of knowledge regarding primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention strategies for childhood cancer survivors at high risk for CHF, drawing on lessons learned from prevention studies in nononcology populations as well as from the more limited experience in cancer survivors.
Figures
References
-
- Lipshultz SE, Alvarez JA, Scully RE. Anthracycline associated cardiotoxicity in survivors of childhood cancer. Heart. 2008;94(4):525–533. - PubMed
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al., editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2008. Bethesda, Md, USA: National Cancer Institute;
-
- Yahalom J, Portlock CS. Long-term cardiac and pulmonary complications of cancer therapy. Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America. 2008;22(2):305–318. - PubMed
-
- Lipshultz SE, Lipsitz SR, Sallan SE, et al. Chronic progressive cardiac dysfunction years after doxorubicin therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(12):2629–2636. - PubMed
-
- van Dalen EC, van der Pal HJH, Kok WEM, Caron HN, Kremer LCM. Clinical heart failure in a cohort of children treated with anthracyclines: a long-term follow-up study. European Journal of Cancer. 2006;42(18):3191–3198. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources