Interactions between genetic background, insulin resistance and β-cell function
- PMID: 22928564
- PMCID: PMC3634618
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01650.x
Interactions between genetic background, insulin resistance and β-cell function
Abstract
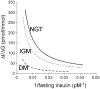
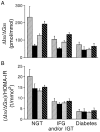
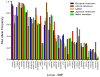
An interaction between genes and the environment is a critical component underlying the pathogenesis of the hyperglycaemia of type 2 diabetes. The development of more sophisticated techniques for studying gene variants and for analysing genetic data has led to the discovery of some 40 genes associated with type 2 diabetes. Most of these genes are related to changes in β-cell function, with a few associated with decreased insulin sensitivity and obesity. Interestingly, using quantitative traits based on continuous measures rather than dichotomous ones, it has become evident that not all genes associated with changes in fasting or post-prandial glucose are also associated with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. Identification of these gene variants has provided novel insights into the physiology and pathophysiology of the β-cell, including the identification of molecules involved in β-cell function that were not previously recognized as playing a role in this critical cell.
Published 2012. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no relevant duality of interest.
Figures
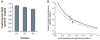
References
-
- Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2003;46:3–19. - PubMed
-
- Florez JC. Newly identified loci highlight beta cell dysfunction as a key cause of type 2 diabetes: where are the insulin resistance genes? Diabetologia. 2008;51:1100–1110. - PubMed
-
- McCarthy MI. Genomics, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2339–2350. - PubMed
-
- Morton GJ, Cummings DE, Baskin DG, Barsh GS, Schwartz MW. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature. 2006;443:289–295. - PubMed
-
- Lam TK, Schwartz GJ, Rossetti L. Hypothalamic sensing of fatty acids. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:579–584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

