Airway smooth muscle in asthma: just a target for bronchodilation?
- PMID: 22929101
- PMCID: PMC3431506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccm.2012.05.002
Airway smooth muscle in asthma: just a target for bronchodilation?
Abstract
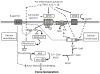
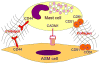
Airway smooth muscle (ASM) has long been recognized as the main cell type responsible for bronchial hyperresponsiveness. It has, thus, been considered as a target for bronchodilation. In asthma, however, there is a complex relationship between ASM and inflammatory cells, such as mast cells and T lymphocytes. Moreover, the increased ASM mass in asthmatic airways is one of the key features of airway remodeling. This article aims to review the main concepts about the 3 possible roles of ASM in asthma: (1) contractile tone, (2) inflammatory response, and (3) remodeling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Busse WW, Lemanske RF., Jr Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:350–62. - PubMed
-
- Huber HL, Koessler KK. The pathology of bronchial asthma. Arch Int Med. 1922;30:689–760.
-
- Bousquet J, Chanez P, Lacoste JY, et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1033–9. - PubMed
-
- Brightling CE, Bradding P, Symon FA, et al. Mast-cell infiltration of airway smooth muscle in asthma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1699–705. - PubMed
-
- Ramos-Barbon D, Fraga-Iriso R, Brienza NS, et al. T Cells localize with proliferating smooth muscle alpha-actin+ cell compartments in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182:317–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

