MLEP: an R package for exploring the maximum likelihood estimates of penetrance parameters
- PMID: 22929166
- PMCID: PMC3537736
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-465
MLEP: an R package for exploring the maximum likelihood estimates of penetrance parameters
Abstract
Background: Linkage analysis is a useful tool for detecting genetic variants that regulate a trait of interest, especially genes associated with a given disease. Although penetrance parameters play an important role in determining gene location, they are assigned arbitrary values according to the researcher's intuition or as estimated by the maximum likelihood principle. Several methods exist by which to evaluate the maximum likelihood estimates of penetrance, although not all of these are supported by software packages and some are biased by marker genotype information, even when disease development is due solely to the genotype of a single allele.
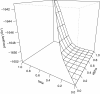
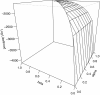
Findings: Programs for exploring the maximum likelihood estimates of penetrance parameters were developed using the R statistical programming language supplemented by external C functions. The software returns a vector of polynomial coefficients of penetrance parameters, representing the likelihood of pedigree data. From the likelihood polynomial supplied by the proposed method, the likelihood value and its gradient can be precisely computed. To reduce the effect of the supplied dataset on the likelihood function, feasible parameter constraints can be introduced into maximum likelihood estimates, thus enabling flexible exploration of the penetrance estimates. An auxiliary program generates a perspective plot allowing visual validation of the model's convergence. The functions are collectively available as the MLEP R package.
Conclusions: Linkage analysis using penetrance parameters estimated by the MLEP package enables feasible localization of a disease locus. This is shown through a simulation study and by demonstrating how the package is used to explore maximum likelihood estimates. Although the input dataset tends to bias the likelihood estimates, the method yields accurate results superior to the analysis using intuitive penetrance values for disease with low allele frequencies. MLEP is part of the Comprehensive R Archive Network and is freely available at http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MLEP/index.html.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Analysis Workshop II: results of incorporating a linkage disequilibrium parameter.Genet Epidemiol. 1984;1(2):179-82. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370010211. Genet Epidemiol. 1984. PMID: 14971367
-
Maximum likelihood estimation of quantitative trait loci parameters with the aid of genetic markers using a standard statistical package.Comput Appl Biosci. 1994 Sep;10(5):513-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.5.513. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994. PMID: 7828067
-
A study comparing precision of the maximum multipoint heterogeneity LOD statistic to three model-free multipoint linkage methods.Genet Epidemiol. 2001 Dec;21(4):315-25. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1037. Genet Epidemiol. 2001. PMID: 11754467
-
Genetic linkage methods for quantitative traits.Stat Methods Med Res. 2001 Feb;10(1):3-25. doi: 10.1177/096228020101000102. Stat Methods Med Res. 2001. PMID: 11329691 Review.
-
A maximum-likelihood estimation of pairwise relatedness for autopolyploids.Heredity (Edinb). 2015 Feb;114(2):133-42. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2014.88. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Heredity (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 25370210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Strauch K. Parametric linkage analysis with automatic optimization of the disease model parameters. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73(Suppl1):A2624.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

