Use of combination chemotherapy for treatment of granulomatous and lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
- PMID: 22930256
- PMCID: PMC3557581
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-012-9755-3
Use of combination chemotherapy for treatment of granulomatous and lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
Abstract
Purpose: A subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) develops granulomatous and lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD), a restrictive lung disease associated with early mortality. The optimal therapy for GLILD is unknown. This study was undertaken to see if rituximab and azathioprine (combination chemotherapy) would improve pulmonary function and/or radiographic abnormalities in patients with CVID and GLILD.
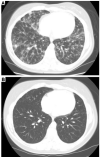
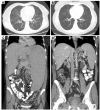
Methods: A retrospective chart review of patients with CVID and GLILD who were treated with combination chemotherapy was performed. Complete pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans of the chest were done prior to therapy and >6 months later. HRCT scans of the chest were blinded, randomized, and scored independently (in pairs) by two radiologists. The differences between pre- and post-treatment HRCT scores and PFT parameters were analyzed.
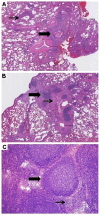
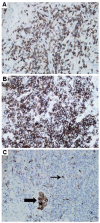
Results: Seven patients with CVID and GLILD met inclusion criteria. Post-treatment increases were noted in both FEV1 (p=0.034) and FVC (p=0.043). HRCT scans of the chest demonstrated improvement in total score (p=0.018), pulmonary consolidations (p=0.041), ground-glass opacities (p=0.020) nodular opacities (p=0.024), and both the presence and extent of bronchial wall thickening (p=0.014, 0.026 respectively). No significant chemotherapy-related complications occurred.
Conclusions: Combination chemotherapy improved pulmonary function and decreased radiographic abnormalities in patients with CVID and GLILD.
Figures
References
-
- Bonilla FA, Bernstein IL, Khan DA, Ballas ZK, Chinen J, Frank MM, et al. Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;94(5 Suppl 1):S1–S63. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham-Rundles C. Common variable immunodeficiency. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001;1(5):421–9. - PubMed
-
- Busse PJ, Razvi S, Cunningham-Rundles C. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in the prevention of pneumonia in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109(6):1001–4. - PubMed
-
- Lucas M, Lee M, Lortan J, Lopez-Granados E, Misbah S, Chapel H. Infection outcomes in patients with common variable immunodeficiency disorders: relationship to immunoglobulin therapy over 22 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125(6):1354–60. e4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

