Graphene: an emerging electronic material
- PMID: 22930422
- PMCID: PMC11524146
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201482
Graphene: an emerging electronic material
Abstract
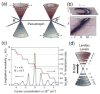
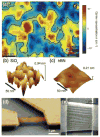
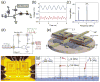
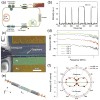
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms in a honeycomb lattice, offers a number of fundamentally superior qualities that make it a promising material for a wide range of applications, particularly in electronic devices. Its unique form factor and exceptional physical properties have the potential to enable an entirely new generation of technologies beyond the limits of conventional materials. The extraordinarily high carrier mobility and saturation velocity can enable a fast switching speed for radio-frequency analog circuits. Unadulterated graphene is a semi-metal, incapable of a true off-state, which typically precludes its applications in digital logic electronics without bandgap engineering. The versatility of graphene-based devices goes beyond conventional transistor circuits and includes flexible and transparent electronics, optoelectronics, sensors, electromechanical systems, and energy technologies. Many challenges remain before this relatively new material becomes commercially viable, but laboratory prototypes have already shown the numerous advantages and novel functionality that graphene provides.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures















References
-
- Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov S, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA. Science. 2004;306:666. - PubMed
-
- Novoselov K, Geim A, Morozov S, Jiang D, Katsnelson M, Grigorieva I, Dubonos S, Firsov A. Nature. 2005;438:197. - PubMed
-
- Geim AK, Novoselov KS. Nat Mater. 2007;6:183. - PubMed
-
- Geim AK. Science. 2009;324:1530. - PubMed
-
- Moore GE. Electronics. 1965;38:114.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

