The reactive stroma microenvironment and prostate cancer progression
- PMID: 22930558
- PMCID: PMC3716392
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-12-0085
The reactive stroma microenvironment and prostate cancer progression
Abstract
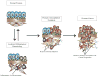
Reactive stroma initiates during early prostate cancer development and coevolves with prostate cancer progression. Previous studies have defined the key markers of reactive stroma and have established that reactive stroma biology influences prostate tumorigenesis and progression. The stem/progenitor cells of origin and the mechanisms that regulate their recruitment and activation to myofibroblasts or carcinoma-associated fibroblasts are essentially unknown. Key regulatory factors have been identified, including transforming growth factor β, interleukin-8, fibroblast growth factors, connective tissue growth factor, wingless homologs-Wnts, and stromal cell-derived factor-1, among others. The biology of reactive stroma in cancer is similar to the more predictable biology of the stroma compartment during wound repair at sites where the epithelial barrier function is breached and a stromal response is generated. The coevolution of reactive stroma and the biology of how reactive stroma-carcinoma interactions regulate cancer progression and metastasis are targets for new therapeutic approaches. Such approaches are strategically designed to inhibit cancer progression by uncoupling the reactive stroma niche.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Abe R, Donnelly SC, Peng T, Bucala R, Metz CN. Peripheral blood fibrocytes: differentiation pathway and migration to wound sites. J Immunol. 2001;166:7556–7562. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed A. The myofibroblast in breast disease. Pathol Annu. 1990;25(Pt 2):237–286. - PubMed
-
- Ao M, Franco OE, Park D, Raman D, Williams K, Hayward SW. Cross-talk between paracrine-acting cytokine and chemokine pathways promotes malignancy in benign human prostatic epithelium. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4244–4253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

