Control of adaptive immune responses by Staphylococcus aureus through IL-10, PD-L1, and TLR2
- PMID: 22930672
- PMCID: PMC3428601
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00606
Control of adaptive immune responses by Staphylococcus aureus through IL-10, PD-L1, and TLR2
Abstract
Microbes induce innate immune responses in hosts. It is critical to know how different microbes control adaptive responses through innate pathways. The impact of gram-positive bacteria on the innate and adaptive responses is unclear. Herein we report that Staphylococcus aureus induces IL-10, Th17-inducing cytokines IL-6 and IL-23, chemokines, and regulates dendritic cell markers. S. aureus inhibits T-cell IL-2 responses through modulation of HLA-DR, CD86 and PD-L1. IFN-gamma, Src kinase inhibitors, or TLR2 antibodies prevented the down-modulation of HLA-DR by S. aureus. Our data demonstrate that innate TLR signaling induces multi-dimensional inhibition of adaptive immune responses, which may contribute to the lack of protective immunity to bacteria or microbe tolerance. IL-10 and PD-L1 antagonists may boost immunity to vaccines for S. aureus and other microbes.
Figures

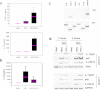
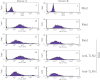
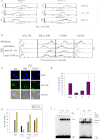


References
-
- Lowy F. D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 339, 520–532 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi O. et al. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity. 11, 443–451 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi O., Hoshino K. & Akira S. Cutting edge: TLR2-deficient and MyD88-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Immunol. 165, 5392–5396 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Adachi O., Ogawa T., Takeda K. & Akira S. Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity. 11, 115–122 (1999). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

