Somatic HIF2A gain-of-function mutations in paraganglioma with polycythemia
- PMID: 22931260
- PMCID: PMC3432945
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1205119
Somatic HIF2A gain-of-function mutations in paraganglioma with polycythemia
Abstract
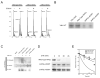
Hypoxia-inducible factors are transcription factors controlling energy, iron metabolism, erythropoiesis, and development. When these proteins are dysregulated, they contribute to tumorigenesis and cancer progression. However, mutations in genes encoding α subunits of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-α) have not previously been identified in any cancer. Here we report two novel somatic gain-of-function mutations in the gene encoding hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF2A) in two patients, one presenting with paraganglioma and the other with paraganglioma and somatostatinoma, both of whom had polycythemia. The two mutations were associated with increased HIF-2α activity and increased protein half-life.
Figures

Comment in
-
HIF2A mutations in paraganglioma with polycythemia.N Engl J Med. 2012 Nov 29;367(22):2161; author reply 2161-2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1211953. N Engl J Med. 2012. PMID: 23190243 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kaelin WG, Jr., Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol Cell. 2008;30:393–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
