Both projection and commissural pathways are disrupted in individuals with chronic stroke: investigating microstructural white matter correlates of motor recovery
- PMID: 22931454
- PMCID: PMC3547772
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-107
Both projection and commissural pathways are disrupted in individuals with chronic stroke: investigating microstructural white matter correlates of motor recovery
Abstract
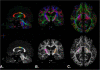
Background: Complete recovery of motor function after stroke is rare with deficits persisting into the chronic phase of recovery. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can evaluate relationships between white matter microstructure and motor function after stroke. The objective of this investigation was to characterize microstructural fiber integrity of motor and sensory regions of the corpus callosum (CC) and descending motor outputs of the posterior limb of the internal capsule (PLIC) in individuals with chronic stroke and evaluate the relationships between white matter integrity and motor function.
Results: Standardized measures of upper extremity motor function were measured in thirteen individuals with chronic stroke. Manual dexterity was assessed in thirteen healthy age-matched control participants. DTI scans were completed for each participant. Fractional anisotropy (FA) of a cross-section of sensory and motor regions of the CC and the PLIC bilaterally were quantified. Multivariate analysis of variance evaluated differences between stroke and healthy groups. Correlational analyses were conducted for measures of motor function and FA. The stroke group exhibited reduced FA in the sensory (p = 0.001) region of the CC, contra- (p = 0.032) and ipsilesional (p = 0.001) PLIC, but not the motor region of the CC (p = 0.236). In the stroke group, significant correlations between contralesional PLIC FA and level of physical impairment (p = 0.005), grip strength (p = 0.006) and hand dexterity (p = 0.036) were observed.
Conclusions: Microstructural status of the sensory region of the CC is reduced in chronic stroke. Future work is needed to explore relationships between callosal sensorimotor fiber integrity and interhemispheric interactions post-stroke. In addition, contralesional primary motor output tract integrity is uniquely and closely associated with multiple dimensions of motor recovery in the chronic phase of stroke suggesting it may be an important biomarker of overall motor recovery.
Figures
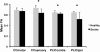

Similar articles
-
Motor skill learning is associated with diffusion characteristics of white matter in individuals with chronic stroke.J Neurol Phys Ther. 2014 Jul;38(3):151-60. doi: 10.1097/NPT.0b013e3182a3d353. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2014. PMID: 23934017 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing the reproducibility of two approaches to quantify white matter tract integrity in stroke.Neuroimage. 2012 Feb 1;59(3):2393-400. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.009. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 21945470 Free PMC article.
-
White matter integrity is a stronger predictor of motor function than BOLD response in patients with stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011 Mar-Apr;25(3):275-84. doi: 10.1177/1545968310389183. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011. PMID: 21357529 Free PMC article.
-
Motor recovery and microstructural change in rubro-spinal tract in subcortical stroke.Neuroimage Clin. 2013 Dec 13;4:201-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.12.003. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2013. PMID: 24432247 Free PMC article.
-
Ten problems and solutions when predicting individual outcome from lesion site after stroke.Neuroimage. 2017 Jan 15;145(Pt B):200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27502048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of corticospinal and extrapyramidal pathways in motor impairment after stroke.Brain Commun. 2022 Nov 21;5(1):fcac301. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac301. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 36601620 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of white matter myelin water fraction in chronic stroke.Neuroimage Clin. 2013 Apr 21;2:569-80. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.04.006. eCollection 2013. Neuroimage Clin. 2013. PMID: 24179808 Free PMC article.
-
Kinematic Measures of Bimanual Performance are Associated With Callosum White Matter Change in People With Chronic Stroke.Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2020 Jul 18;2(4):100075. doi: 10.1016/j.arrct.2020.100075. eCollection 2020 Dec. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2020. PMID: 33543100 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased white matter fractional anisotropy is associated with poorer functional motor skills following spinal cord injury: a pilot study.Spinal Cord. 2019 Mar;57(3):206-213. doi: 10.1038/s41393-018-0191-y. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Spinal Cord. 2019. PMID: 30185892
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Evaluation of Neural Network Development in Patients Undergoing Therapeutic Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation following Stroke.Neural Plast. 2018 Mar 13;2018:3901016. doi: 10.1155/2018/3901016. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29725347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gresham GE, Duncan PW, Stason WB, Adams HP, Adelman AM, Alexander DN, Bishop DS, Diller L, Donaldson NE, Granger CV, Holland AL, Kellyhayes M, McDowell FH, Phipps MA, Roth EJ, Siebens HC, Tarvin GA, Trombly CA. Post-stroke rehabilitation - assessment, referral and patient management. Am Fam Physician. 1995;52(2):461–470. - PubMed
-
- Carey JR, Kimberley TJ, Lewis SM, Auerbach EJ, Dorsey L, Rundquist P, Ugurbil K. Analysis of fMRI and finger tracking training in subjects with chronic stroke. Brain. 2002;125(Pt 4):773–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

