Using formative research to develop the healthy eating component of the CHANGE! school-based curriculum intervention
- PMID: 22931457
- PMCID: PMC3548762
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-710
Using formative research to develop the healthy eating component of the CHANGE! school-based curriculum intervention
Abstract
Background: Childhood obesity is a significant public health concern. Many intervention studies have attempted to combat childhood obesity, often in the absence of formative or preparatory work. This study describes the healthy eating component of the formative phase of the Children's Health Activity and Nutrition: Get Educated! (CHANGE!) project. The aim of the present study was to gather qualitative focus group and interview data regarding healthy eating particularly in relation to enabling and influencing factors, barriers and knowledge in children and adults (parents and teachers) from schools within the CHANGE! programme to provide population-specific evidence to inform the subsequent intervention design.
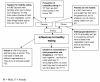
Methods: Semi-structured focus group interviews were conducted with children, parents and teachers across 11 primary schools in the Wigan borough of North West England. Sixty children (N = 24 boys), 33 parents (N = 4 male) and 10 teachers (N = 4 male) participated in the study. Interview questions were structured around the PRECEDE phases of the PRECEDE-PROCEED model. Interviews were transcribed verbatim and analysed using the pen-profiling technique.
Results: The pen-profiles revealed that children's knowledge of healthy eating was generally good, specifically many children were aware that fruit and vegetable consumption was 'healthy' (N = 46). Adults' knowledge was also good, including restricting fatty foods, promoting fruit and vegetable intake, and maintaining a balanced diet. The important role parents play in children's eating behaviours and food intake was evident. The emerging themes relating to barriers to healthy eating showed that external drivers such as advertising, the preferred sensory experience of "unhealthy" foods, and food being used as a reward may play a role in preventing healthy eating.
Conclusions: Data suggest that; knowledge related to diet composition was not a barrier per se to healthy eating, and education showing how to translate knowledge into behavior or action is required. The key themes that emerged through the focus groups and pen-profiling data analysis technique will be used to inform and tailor the healthy eating component of the CHANGE! intervention study.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN03863885
Figures





Similar articles
-
Using formative research to develop CHANGE!: a curriculum-based physical activity promoting intervention.BMC Public Health. 2011 Oct 27;11:831. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-831. BMC Public Health. 2011. PMID: 22032540 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting healthy weight in primary school children through physical activity and nutrition education: a pragmatic evaluation of the CHANGE! randomised intervention study.BMC Public Health. 2013 Jul 2;13:626. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-626. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23819701 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
School-based intervention that integrates nutrition education and supportive healthy school food environment among Malaysian primary school children: a study protocol.BMC Public Health. 2019 Oct 30;19(1):1427. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7708-y. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31666034 Free PMC article.
-
[Simple obesity in children. A study on the role of nutritional factors].Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):3-191. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006. PMID: 16733288 Review. Polish.
-
Family environmental factors influencing the developing behavioral controls of food intake and childhood overweight.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2001 Aug;48(4):893-907. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(05)70347-3. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11494642 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Perceptions of Inspiratory Muscle Training in Children With Cystic Fibrosis and Their Multidisciplinary Team: Mixed-Methods Study.JMIR Pediatr Parent. 2018 Oct 25;1(2):e11189. doi: 10.2196/11189. JMIR Pediatr Parent. 2018. PMID: 31518290 Free PMC article.
-
The Tangibility of Personalized 3D-Printed Feedback May Enhance Youths' Physical Activity Awareness, Goal Setting, and Motivation: Intervention Study.J Med Internet Res. 2019 May 31;21(6):e12067. doi: 10.2196/12067. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31199322 Free PMC article.
-
Engagement, Acceptability, Usability, and Preliminary Efficacy of a Self-Monitoring Mobile Health Intervention to Reduce Sedentary Behavior in Belgian Older Adults: Mixed Methods Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Oct 29;8(10):e18653. doi: 10.2196/18653. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 33118951 Free PMC article.
-
Jump2Health Website™ for Head Start parents to promote a healthy home environment: Results from formative research.J Public Health Res. 2017 Dec 13;6(3):1054. doi: 10.4081/jphr.2017.1054. eCollection 2017 Dec 13. J Public Health Res. 2017. PMID: 29291193 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of a High-Intensity PrO2Fit Inspiratory Muscle Training Intervention on Physiological and Psychological Health in Adults with Bronchiectasis: A Mixed-Methods Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 16;18(6):3051. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063051. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33809595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canoy D, Buchan I. Challenges in obesity epidemiology. Obes Rev. 2007;8(Suppl 1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health. Choosing a better diet. London; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

