Control of fluoroquinolone resistance through successful regulation, Australia
- PMID: 22932272
- PMCID: PMC3437704
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1809.111515
Control of fluoroquinolone resistance through successful regulation, Australia
Abstract
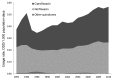
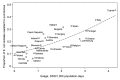
Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial drugs are highly bioavailable, broad-spectrum agents with activity against gram-negative pathogens, especially those resistant to other classes of antimicrobial drugs. Australia has restricted the use of quinolones in humans through its national pharmaceutical subsidy scheme; and, through regulation, has not permitted the use of quinolones in food-producing animals. As a consequence, resistance to fluoroquinolones in the community has been slow to emerge and has remained at low levels in key pathogens, such as Escherichia coli. In contrast to policies in most other countries, this policy has successfully preserved the utility of this class of antimicrobial drugs for treatment of most infections.
Figures
References
-
- Horcajada JP, Vila J, Moreno-Martinez A, Ruiz J, Martinez JA, Sanchez M, et al. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of resistance to quinolones in Escherichia coli after prolonged administration of ciprofloxacin in patients with prostatitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;49:55–9. 10.1093/jac/49.1.55 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
