Kv4.2 potassium channels segregate to extrasynaptic domains and influence intrasynaptic NMDA receptor NR2B subunit expression
- PMID: 22932868
- PMCID: PMC3748322
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-012-0450-1
Kv4.2 potassium channels segregate to extrasynaptic domains and influence intrasynaptic NMDA receptor NR2B subunit expression
Abstract
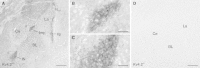
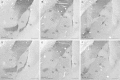
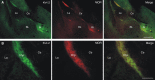
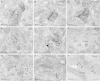
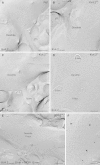
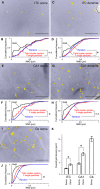
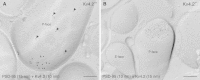
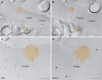
Neurons of the intercalated cell clusters (ITCs) represent an important relay site for information flow within amygdala nuclei. These neurons receive mainly glutamatergic inputs from the basolateral amygdala at their dendritic domains and provide feed-forward inhibition to the central nucleus. Voltage-gated potassium channels type-4.2 (Kv4.2) are main players in dendritic signal processing and integration providing a key component of the A currents. In this study, the subcellular localization and distribution of the Kv4.2 was studied in ITC neurons by means of light- and electron microscopy, and compared to other types of central principal neurons. Several ultrastructural immunolocalization techniques were applied including pre-embedding techniques and, most importantly, SDS-digested freeze-fracture replica labeling. We found Kv4.2 densely expressed in somato-dendritic domains of ITC neurons where they show a differential distribution pattern as revealed by nearest neighbor analysis. Comparing ITC neurons with hippocampal pyramidal and cerebellar granule cells, a cell type- and domain-dependent organization in Kv4.2 distribution was observed. Kv4.2 subunits were localized to extrasynaptic sites where they were found to influence intrasynaptic NMDA receptor subunit expression. In samples of Kv4.2 knockout mice, the frequency of NR1-positive synapses containing the NR2B subunit was significantly increased. This indicates a strong, yet indirect effect of Kv4.2 on the synaptic content of NMDA receptor subtypes, and a likely role in synaptic plasticity at ITC neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corticotropin-releasing factor in the mouse central nucleus of the amygdala: ultrastructural distribution in NMDA-NR1 receptor subunit expressing neurons as well as projection neurons to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.Exp Neurol. 2013 Jan;239:120-32. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23063907 Free PMC article.
-
Mossy fibre contact triggers the targeting of Kv4.2 potassium channels to dendrites and synapses in developing cerebellar granule neurons.J Neurochem. 2004 May;89(4):897-907. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02368.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15140189
-
Downregulation of Kv4.2 channels mediated by NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons.Neuroscience. 2010 Jan 20;165(2):350-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.041. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19857555 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, bidirectional remodeling of synaptic NMDA receptor subunit composition by A-type K+ channel activity in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.Neuron. 2008 Nov 26;60(4):657-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.029. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 19038222 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of glutamate transporters couples to Kv4.2 dephosphorylation through activation of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors.Neuroscience. 2010 Jan 13;165(1):130-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.024. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19850106 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Calcium signalling in medial intercalated cell dendrites and spines.J Physiol. 2017 Aug 15;595(16):5653-5669. doi: 10.1113/JP274261. Epub 2017 Jul 16. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28594440 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroplasticity of A-type potassium channel complexes induced by chronic alcohol exposure enhances dendritic calcium transients in hippocampus.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Jun;232(11):1995-2006. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3835-4. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25510858 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiology of Dendritic Spines: Information Processing, Dynamic Compartmentalization, and Synaptic Plasticity.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;34:103-141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-36159-3_3. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37962795
-
FMRP Mediates Chronic Ethanol-Induced Changes in NMDA, Kv4.2, and KChIP3 Expression in the Hippocampus.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Jun;40(6):1251-61. doi: 10.1111/acer.13060. Epub 2016 May 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27147118 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory mechanisms and multiple functions of somatodendritic A-type K (+) channel auxiliary subunits.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Mar 27;8:82. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00082. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24723849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

