Trafficking and replication patterns reveal splenic macrophages as major targets of dengue virus in mice
- PMID: 22933295
- PMCID: PMC3486461
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00375-12
Trafficking and replication patterns reveal splenic macrophages as major targets of dengue virus in mice
Abstract
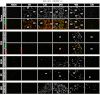
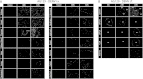
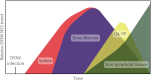
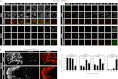
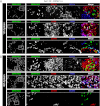
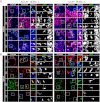
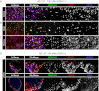
Human postmortem studies of natural dengue virus (DENV) infection have reported systemically distributed viral antigen. Although it is widely accepted that DENV infects mononuclear phagocytes, the sequence in which specific tissues and cell types are targeted remains uncharacterized. We previously reported that mice lacking alpha/beta and gamma interferon receptors permit high levels of DENV replication and show signs of systemic disease (T. R. Prestwood et al., J. Virol. 82:8411-8421, 2008). Here we demonstrate that within 6 h, DENV traffics to and replicates in both CD169(+) and SIGN-R1(+) macrophages of the splenic marginal zone or draining lymph node, respectively, following intravenous or intrafootpad inoculation. Subsequently, high levels of replication are detected in F4/80(+) splenic red pulp macrophages and in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches. Intravenously inoculated mice begin to succumb to dengue disease 72 h after infection, at which time viral replication occurs systemically, except in lymphoid tissues. In particular, high levels of replication occur in CD68(+) macrophages of the kidneys, heart, thymus, and gastrointestinal tract. Over the course of infection, proportionately large quantities of DENV traffic to the liver and spleen. However, late during infection, viral trafficking to the spleen decreases, while trafficking to the liver, thymus, and kidneys increases. The present study demonstrates that macrophage populations, initially in the spleen and other lymphoid tissues and later in nonlymphoid tissues, are major targets of DENV infection in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Balsitis SJ, et al. 2009. Tropism of dengue virus in mice and humans defined by viral nonstructural protein 3-specific immunostaining. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 80:416–424 - PubMed
-
- Bhoopat L, et al. 1996. Immunohistochemical characterization of a new monoclonal antibody reactive with dengue virus-infected cells in frozen tissue using immunoperoxidase technique. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 14:107–113 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

