Ultrasensitive allele-specific PCR reveals rare preexisting drug-resistant variants and a large replicating virus population in macaques infected with a simian immunodeficiency virus containing human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase
- PMID: 22933296
- PMCID: PMC3497681
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01963-12
Ultrasensitive allele-specific PCR reveals rare preexisting drug-resistant variants and a large replicating virus population in macaques infected with a simian immunodeficiency virus containing human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase
Abstract
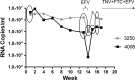
It has been proposed that most drug-resistant mutants, resulting from a single-nucleotide change, exist at low frequency in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) populations in vivo prior to the initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART). To test this hypothesis and to investigate the emergence of resistant mutants with drug selection, we developed a new ultrasensitive allele-specific PCR (UsASP) assay, which can detect drug resistance mutations at a frequency of ≥0.001% of the virus population. We applied this assay to plasma samples obtained from macaques infected with an SIV variant containing HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) (RT-simian-human immunodeficiency [SHIV](mne)), before and after they were exposed to a short course of efavirenz (EFV) monotherapy. We detected RT inhibitor (RTI) resistance mutations K65R and M184I but not K103N in 2 of 2 RT-SHIV-infected macaques prior to EFV exposure. After three doses over 4 days of EFV monotherapy, 103N mutations (AAC and AAT) rapidly emerged and increased in the population to levels of ∼20%, indicating that they were present prior to EFV exposure. The rapid increase of 103N mutations from <0.001% to 20% of the viral population indicates that the replicating virus population size in RT-SHIV-infected macaques must be 10(6) or more infected cells per replication cycle.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

