Determinants of hepatitis A vaccine immunity in a cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected children living in Switzerland
- PMID: 22933400
- PMCID: PMC3491535
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00264-12
Determinants of hepatitis A vaccine immunity in a cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected children living in Switzerland
Abstract
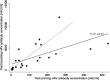
Vaccination in HIV-infected children is often less effective than in healthy children. The goal of this study was to assess vaccine responses to hepatitis A virus (HAV) in HIV-infected children. Children of the Swiss Mother and Child HIV Cohort Study (MoCHiV) were enrolled prospectively. Recommendations for initial, catch-up, and additional HAV immunizations were based upon baseline antibody concentrations and vaccine history. HAV IgG was assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with a protective cutoff value defined as ≥10 mIU/ml. Eighty-seven patients were included (median age, 11 years; range, 3.4 to 21.2 years). Forty-two patients were seropositive (48.3%) for HAV. Among 45 (51.7%) seronegative patients, 36 had not received any HAV vaccine dose and were considered naïve. Vaccine responses were assessed after the first dose in 29/35 naïve patients and after the second dose in 33/39 children (25 initially naïve patients, 4 seronegative patients, and 4 seropositive patients that had already received 1 dose of vaccine). Seroconversion was 86% after 1 dose and 97% after 2 doses, with a geometric mean concentration of 962 mIU/ml after the second dose. A baseline CD4(+) T cell count below 750 cells/μl significantly reduced the post-2nd-dose response (P = 0.005). Despite a high rate of seroconversion, patients with CD4(+) T cell counts of <750/μl had lower anti-HAV antibody concentrations. This may translate into a shorter protection time. Hence, monitoring humoral immunity may be necessary to provide supplementary doses as needed.
Figures



References
-
- Abarca K, Ibánez I, Perret C, Vial P, Zinsou J-A. 2008. Immunogenicity, safety, and interchangeability of two inactivated hepatitis A vaccines in Chilean children. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 12:270–277 - PubMed
-
- Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), Fiore AE, Wasley A, Bell BP. 2006. Prevention of hepatitis A through active or passive immunization: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recommend. Rep. 55:1–23 - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, et al. 2005. Prevalence and risk factors of hepatitis A infection in an HIV-infected French population. Med. Mal. Infect. 35:73–81 (In French.) - PubMed
-
- Cagigi A, et al. 2008. Altered expression of the receptor-ligand pair CXCR5/CXCL13 in B cells during chronic HIV-1 infection. Blood 112:4401–4410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

