DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 22933559
- PMCID: PMC3429619
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.05020-11
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
From microbes to multicellular eukaryotic organisms, all cells contain pathways responsible for genome maintenance. DNA replication allows for the faithful duplication of the genome, whereas DNA repair pathways preserve DNA integrity in response to damage originating from endogenous and exogenous sources. The basic pathways important for DNA replication and repair are often conserved throughout biology. In bacteria, high-fidelity repair is balanced with low-fidelity repair and mutagenesis. Such a balance is important for maintaining viability while providing an opportunity for the advantageous selection of mutations when faced with a changing environment. Over the last decade, studies of DNA repair pathways in bacteria have demonstrated considerable differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. Here we review and discuss the DNA repair, genome maintenance, and DNA damage checkpoint pathways of the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. We present their molecular mechanisms and compare the functions and regulation of several pathways with known information on other organisms. We also discuss DNA repair during different growth phases and the developmental program of sporulation. In summary, we present a review of the function, regulation, and molecular mechanisms of DNA repair and mutagenesis in Gram-positive bacteria, with a strong emphasis on B. subtilis.
Figures
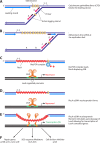
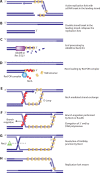
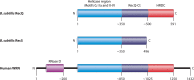


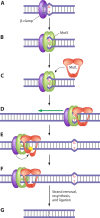
References
-
- Aamodt RM, Falnes PO, Johansen RF, Seeberg E, Bjoras M. 2004. The Bacillus subtilis counterpart of the mammalian 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase has hypoxanthine and 1,N6-ethenoadenine as preferred substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 279:13601–13606 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JC, Stiege AC, Luder G. 1993. Genetic recombination in Bacillus subtilis 168: effect of recN, recF, recH and addAB mutations on DNA repair and recombination. Mol. Gen. Genet. 239:129–136 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

