Neuromodulator-evoked synaptic metaplasticity within a central pattern generator network
- PMID: 22933725
- PMCID: PMC3545119
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00586.2012
Neuromodulator-evoked synaptic metaplasticity within a central pattern generator network
Abstract
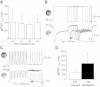
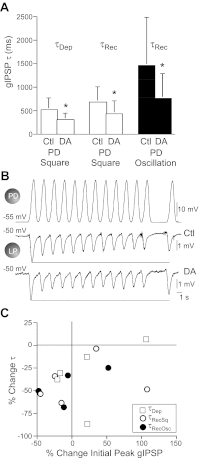
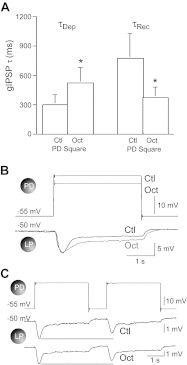
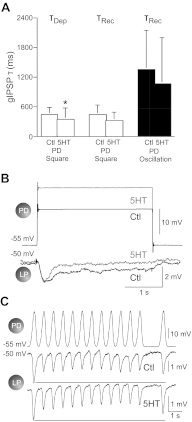
Synapses show short-term activity-dependent dynamics that alter the strength of neuronal interactions. This synaptic plasticity can be tuned by neuromodulation as a form of metaplasticity. We examined neuromodulator-induced metaplasticity at a graded chemical synapse in a model central pattern generator (CPG), the pyloric network of the spiny lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Dopamine, serotonin, and octopamine each produce a unique motor pattern from the pyloric network, partially through their modulation of synaptic strength in the network. We characterized synaptic depression and its amine modulation at the graded synapse from the pyloric dilator neuron to the lateral pyloric neuron (PD→LP synapse), driving the PD neuron with both long square pulses and trains of realistic waveforms over a range of presynaptic voltages. We found that the three amines can differentially affect the amplitude of graded synaptic transmission independently of the synaptic dynamics. Low concentrations of dopamine had weak and variable effects on the strength of the graded inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (gIPSPs) but reliably accelerated the onset of synaptic depression and recovery from depression independently of gIPSP amplitude. Octopamine enhanced gIPSP amplitude but decreased the amount of synaptic depression; it slowed the onset of depression and accelerated its recovery during square pulse stimulation. Serotonin reduced gIPSP amplitude but increased the amount of synaptic depression and accelerated the onset of depression. These results suggest that amine-induced metaplasticity at graded chemical synapses can alter the parameters of synaptic dynamics in multiple and independent ways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distributed amine modulation of graded chemical transmission in the pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion.J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jul;74(1):437-52. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.1.437. J Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 7472345
-
Amine modulation of glutamate responses from pyloric motor neurons in lobster stomatogastric ganglion.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Dec;78(6):3210-21. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.6.3210. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9405540
-
Aminergic modulation of graded synaptic transmission in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion.J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2066-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02066.1990. J Neurosci. 1990. PMID: 2165519 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed effects of dopamine modulation in the crustacean pyloric network.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Nov 16;860:155-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09046.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9928309 Review.
-
Oscillations and oscillatory behavior in small neural circuits.Biol Cybern. 2006 Dec;95(6):537-54. doi: 10.1007/s00422-006-0125-1. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Biol Cybern. 2006. PMID: 17151878 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and developmental expression of the enzymes responsible for dopamine, histamine, octopamine and serotonin biosynthesis in the copepod crustacean Calanus finmarchicus.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 1;195:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 19. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24148657 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term synaptic dynamics control the activity phase of neurons in an oscillatory network.Elife. 2019 Jun 10;8:e46911. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46911. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31180323 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of endogenous neuromodulators in a small motor network enhances responsiveness to neuromodulation.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Sep 1;118(3):1749-1761. doi: 10.1152/jn.00383.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28659465 Free PMC article.
-
The complexity of small circuits: the stomatogastric nervous system.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016 Dec;41:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27450880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine: a parallel pathway for the modulation of spinal locomotor networks.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Jun 16;8:55. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00055. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 24982614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott LF, Regehr WG. Synaptic computation. Nature 431: 796–803, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Ayali A, Harris-Warrick RM. Interaction of dopamine and cardiac sac modulatory inputs on the pyloric network in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Brain Res 794: 155–161, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bidaut M. Pharmacological dissection of the pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion using picrotoxin. J Neurophysiol 44: 1089–1101, 1980 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

