Extreme delta brush: a unique EEG pattern in adults with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis
- PMID: 22933737
- PMCID: PMC3525298
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182698cd8
Extreme delta brush: a unique EEG pattern in adults with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis
Abstract
Objectives: To determine continuous EEG (cEEG) patterns that may be unique to anti-NMDA receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis in a series of adult patients with this disorder.
Methods: We evaluated the clinical and EEG data of 23 hospitalized adult patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis who underwent cEEG monitoring between January 2005 and February 2011 at 2 large academic medical centers.
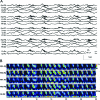
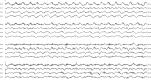
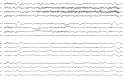
Results: Twenty-three patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis underwent a median of 7 (range 1-123) days of cEEG monitoring. The median length of hospitalization was 44 (range 2-200) days. Personality or behavioral changes (100%), movement disorders (82.6%), and seizures (78.3%) were the most common symptoms. Seven of 23 patients (30.4%) had a unique electrographic pattern, which we named "extreme delta brush" because of its resemblance to waveforms seen in premature infants. The presence of extreme delta brush was associated with a more prolonged hospitalization (mean 128.3 ± 47.5 vs 43.2 ± 39.0 days, p = 0.008) and increased days of cEEG monitoring (mean 27.6 ± 42.3 vs 6.2 ± 5.6 days, p = 0.012). The modified Rankin Scale score showed a trend toward worse scores in patients with the extreme delta brush pattern (mean 4.0 ± 0.8 vs 3.1 ± 1.1, p = 0.089).
Conclusions: Extreme delta brush is a novel EEG finding seen in many patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis. The presence of this pattern is associated with a more prolonged illness. Although the specificity of this pattern is unclear, its presence should raise consideration of this syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EEG extreme delta brush: An ictal pattern in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 Aug;49:280-5. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.04.032. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 26071995 Clinical Trial.
-
Ictal Rhythmic Alpha Sinusoidal Waves in 3 Cases of Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2018 Sep;49(5):302-305. doi: 10.1177/1550059417745185. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29186977
-
Extreme delta brush guides to the diagnosis of anti-NMDAR encephalitis.J Neurol Sci. 2015;353(1-2):81-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25921549
-
EEG findings in NMDA encephalitis - A systematic review.Seizure. 2019 Feb;65:20-24. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2018.12.015. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Seizure. 2019. PMID: 30597400
-
Understanding Seizures and Prognosis of the Extreme Delta Brush Pattern in Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Encephalitis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2021 Sep 21;13(9):e18154. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18154. eCollection 2021 Sep. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34589370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep Disturbances Associated with Neurological Autoimmunity.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jan;18(1):181-201. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01020-x. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33786802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Mechanisms in Epileptogenesis: Update on Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Epilepsy Syndromes.Drugs. 2023 Feb;83(2):135-158. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01826-9. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36696027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmune encephalitis and epilepsy: evolving definition and clinical spectrum.Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020 Aug;63(8):291-300. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2019.00598. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31431603 Free PMC article.
-
[Intensive care aspects of autoimmune encephalitis].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2019 Oct;114(7):620-627. doi: 10.1007/s00063-019-0604-5. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2019. PMID: 31456008 Review. German.
-
[Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes and autoimmune encephalitis].Nervenarzt. 2014 Apr;85(4):485-98; quiz 499-501. doi: 10.1007/s00115-014-4030-x. Nervenarzt. 2014. PMID: 24668402 Review. German.
References
-
- Pruss H, Dalmau J, Harms L, et al. Retrospective analysis of NMDA receptor antibodies in encephalitis of unknown origin. Neurology 2010;75:1735–1739 - PubMed
-
- Clancy RR, Bergqvist AGC, Dlugos DJ. Neonatal Electroencephalography. In: Ebersole JS, Pedley TA, eds. Current Practice of Clinical Electroencephalography, 3rd ed Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003:160−234
-
- Chong DJ, Hirsch LJ. Which EEG patterns warrant treatment in the critically ill? Reviewing the evidence for treatment of periodic epileptiform discharges and related patterns. J Clin Neurophysiol 22:79–91, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
