Radiolabeled somatostatin analogues therapy in advanced neuroendocrine tumors: a single centre experience
- PMID: 22934111
- PMCID: PMC3425839
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/320198
Radiolabeled somatostatin analogues therapy in advanced neuroendocrine tumors: a single centre experience
Abstract
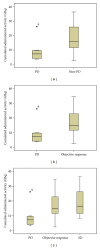
The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of PRRT in patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). Patients and Methods. From January 2007 to August 2011, we enrolled 65 patients (m/f 38/27; mean age 65 years, range 33-83) with advanced NETs having enhanced SSTR expression, treated with PRRT. The enhanced expression of SSTR was assessed using (68)Ga-DOTATOC/DOTATATE PET/CT. Among all the enrolled patients, 6 of them were excluded from the present analysis since they voluntarily interrupted treatment. Mean activity/cycle of 2.6 GBq ((90)Y-DOTATOC/DOTATATE) or 6.0 GBq ((177)Lu-DOTATOC/DOTATATE) was administrated intravenously (max 9 cycles). Results. Complete response (CR) was found in 1/59 (2%) patients, partial remission (PR) in 24/59 (40.5%) patients, stable disease (SD) in 24/59 (40.5%), and progression (PD) in 10/59 (17%) patients. The overall tumor response rate (CR + PR) was 42.5%. In 40.5% of patients, the disease could be stabilized. Overall, 49 out of 59 patients had no tumor progression (83%). Twelve patients out of 59 (20%) had grade 2-3 hematological side effects including anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia. Long-term nephrotoxicity was observed in 3 patients (2 moderate, 1 severe). Conclusions. PRRT is a promising perspective for patients with advanced NETs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Initial clinical evaluation of indigenous 90Y-DOTATATE in sequential duo-PRRT approach (177Lu-DOTATATE and 90Y-DOTATATE) in neuroendocrine tumors with large bulky disease: Observation on tolerability, 90Y-DOTATATE post- PRRT imaging characteristics (bremsstrahlung and PETCT) and early adverse effects.World J Nucl Med. 2020 Oct 2;20(1):73-81. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_52_20. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. World J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 33850492 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy Using 177 Lu-DOTATATE in Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs) in a Limited-Resource Environment.World J Nucl Med. 2022 Aug 16;21(3):215-221. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1755412. eCollection 2022 Sep. World J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 36060085 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of hitherto unknown brain meningioma detected on 68Ga-DOTATATE positron-emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumor and exploring potential of 177Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy as single-shot treatment approach targeting both tumors.World J Nucl Med. 2019 Apr-Jun;18(2):160-170. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_39_18. World J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 31040748 Free PMC article.
-
Use of radioactive substances in diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun;50(6):740-7. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2015.1033454. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25959100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic efficacy of 177Lu-DOTATATE/DOTATOC in advanced neuroendocrine tumors: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(10):e19304. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019304. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32150065 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kidney dosimetry in ¹⁷⁷Lu and ⁹⁰Y peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: influence of image timing, time-activity integration method, and risk factors.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:935351. doi: 10.1155/2013/935351. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23865075 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prediction of lesion-based response to PRRT using baseline somatostatin receptor PET.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 14;12:1523862. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1523862. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40160333 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of dose with toxicity and tumour response to 90Y- and 177Lu-PRRT provides the basis for optimization through individualized treatment planning.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018 Dec;45(13):2426-2441. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-4044-x. Epub 2018 May 21. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29785514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: a Single-Centre Experience.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Feb;55(1):38-45. doi: 10.1007/s13139-020-00679-y. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33643488 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled Somatostatin Analogues for Diagnosis and Treatment of Neuroendocrine Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;14(4):1055. doi: 10.3390/cancers14041055. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26(18):3063–3072. - PubMed
-
- Bodei L, Ferone D, Grana CM, et al. Peptide receptor therapies in neuroendocrine tumors. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. 2009;32(4):360–369. - PubMed
-
- Kaltsas GA, Rockall A, Papadogias D, Reznek R, Grossman AB. Recent advances in radiological and radionuclide imaging and therapy of neuroendocrine tumours. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2004;151(1):15–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

