Contralateral breast metastasis from pulmonary adenocarcinoma: two cases report and literature review
- PMID: 22934141
- PMCID: PMC3426735
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.02.03
Contralateral breast metastasis from pulmonary adenocarcinoma: two cases report and literature review
Abstract
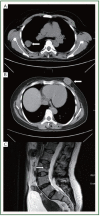
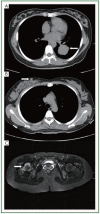
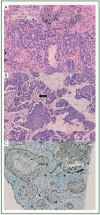
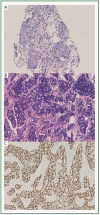
Carcinoma metastatic to breast from extra-mammary malignancy is rare and only accounts for 0.4-1.3% of all breast cancer. Two rare cases of single breast metastasis from pulmonary adenocarcinoma were reported here with a brief review of the pertinent literature. The only complaint of the these two female patients was painless breast mass found recently. Most breast metastasis previously reported are present in the upper outer quadrant, however, in our study, one case was found to be located in the lower inner quadrant and the other in the upper inner quadrant. Tumor cells from breast biopsy were immune-positive for thyroid transcription factor-1. The two patients survived 5 and 8 months, respectively, following the diagnosis of both the primary lung tumor and the breast metastasis. Breast metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma is rare but does exist. The awareness of this possibility may help to differentiate the tumor from primary breast carcinoma. Clinical history and immunohistochemical studies are essential to reach the final diagnosis.
Keywords: Lung neoplasms; breast neoplasm; neoplasm metastasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ipsilateral breast metastasis from a pulmonary adenocarcinoma: a case report and a focused review of the literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9647-54. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast metastasis from lung cancer: a report of two cases and literature review.Cancer Biol Med. 2014 Sep;11(3):208-15. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.03.007. Cancer Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 25364582 Free PMC article.
-
Folliculotropic Cutaneous Metastases and Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa: When Cutaneous Metastases of Breast Carcinoma Are Mistaken for Cutaneous Infections.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016 Jun;24(2):154-7. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016. PMID: 27477179
-
Breast metastasis from a pulmonary adenocarcinoma: Case report and review of the literature.Oncol Lett. 2013 Jan;5(1):328-332. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.995. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Oncol Lett. 2013. Retraction in: Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):6305. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10965. PMID: 23255943 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Metastasis to the breast from an adenocarcinoma of the lung with extensive micropapillary component: a case report and review of the literature.Diagn Pathol. 2010 Dec 17;5:82. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-5-82. Diagn Pathol. 2010. PMID: 21167048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ipsilateral breast metastasis from a pulmonary adenocarcinoma: a case report and a focused review of the literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9647-54. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature.Front Oncol. 2024 May 22;14:1370453. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1370453. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38841167 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Breast Metastasis from a Primary Lung Tumor: Case Report.Curr Oncol. 2024 Aug 16;31(8):4695-4703. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31080350. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39195333 Free PMC article.
-
'Inflammatory breast cancer' due to metastatic adenocarcinoma of lung.BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Sep 1;2016:bcr2016215857. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-215857. BMJ Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27587745 Free PMC article.
-
Breast metastases from primary lung cancer: a retrospective case series on clinical, ultrasonographic, and immunohistochemical features.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Jul;10(7):3226-3235. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-542. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34430360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee SH, Park JM, Kook SH, et al. Metastatic tumors to the breast: mammographic and ultrasonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med 2000;19:257-62 - PubMed
-
- Yeh CN, Lin CH, Chen MF. Clinical and ultrasonographic characteristics of breast metastases from extramammary malignancies. Am Surg 2004;70:287-90 - PubMed
-
- Fulciniti F, Losito S, Botti G, et al. Metastases to the breast: role of fine needle cytology samples. Our experience with nine cases in 2 years. Ann Oncol 2008;19:682-7 - PubMed
-
- Klingen TA, Klaasen H, Aas H, et al. Secondary breast cancer: a 5-year population-based study with review of the literature. APMIS 2009;117:762-7 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
