DNA topoisomerase I drugs and radiotherapy for lung cancer
- PMID: 22934142
- PMCID: PMC3426746
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.07.12
DNA topoisomerase I drugs and radiotherapy for lung cancer
Abstract
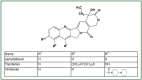
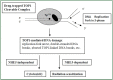
Lung cancer represents the most common cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States and around the world. DNA topoisomerase I (TOP1) drugs such as irinotecan and topotecan represent a unique class of chemotherapeutic agents that exhibit not only potent cytotoxic effect, but also tumor-selective radiation-sensitizing effect. The mechanism of cytotoxicity and radiation sensitization by TOP1 drugs has been intensely investigated. Modern radiotherapy, aided by improved imaging and treatment delivery technology, is capable of targeting tumors more precisely, while sparing surrounding critical structures. Clinical trials with camptothecin derivatives and radiotherapy have been conducted in lung cancers. Combined modality therapy with TOP1 drugs and radiotherapy offers a new frontier for lung cancer therapy. We review the present state of TOP1-targeted chemotherapy and modern radiotherapy for lung cancer.
Keywords: DNA topoisomerase I (TOP1); camptothecin derivative; lung cancer; radiation sensitizer; radiation therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A.Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012;62:10-29 - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011;378:1727-40 - PubMed
-
- van Meerbeeck JP, Fennell DA, De Ruysscher DK. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011;378:1741-55 - PubMed
-
- Principles and Practice of Radiation Oncology. 5th ed., Perez and Brady (eds.), Philadelphia, J. B. Lippincott Co., 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
