Influence of Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) Kuntze on Altered Antioxidant Enzyme Profile during Cutaneous Wound Healing in Immunocompromised Rats
- PMID: 22934192
- PMCID: PMC3425837
- DOI: 10.5402/2012/948792
Influence of Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) Kuntze on Altered Antioxidant Enzyme Profile during Cutaneous Wound Healing in Immunocompromised Rats
Abstract
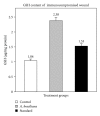
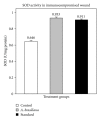
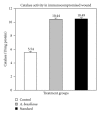
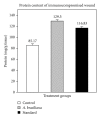
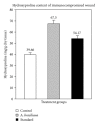
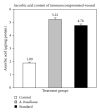
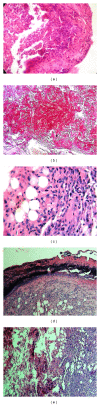
Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) Kuntze (Amaranthaceae) is a herbaceous plant used against inflammation, cough, and diarrhea in Brazilian popular medicine. In our preliminary study, promising wound healing activity of methanol extract of leaves of A. brasiliana (MEAB) was observed in normal excision and incision wound models. Therefore, the present study was designed to investigate the wound healing activity along with the antioxidant enzyme profile during cutaneous excision immunocompromised wound after topical application of 5% w/w ointment of MEAB in rats. Immunocompromised state was induced by pretreatment with hydrocortisone (HC) at 40 mg/kg body weight (i.m.) in male rats. Following one-week pretreatment with HC, wounds were created. The vehicle, 5% (w/w) ointment of MEAB, or standard drug (Himax) was applied topically twice daily. Healing potential was evaluated by the rate of wound contraction, estimation of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants like catalase, SOD, GSH, protein, vitamin C, and hydroxyproline content, which was supported by histopathological study on the 8th day following wounding. There was significant increase in the enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant parameters in the extract-reated group as compared to control group. Histopathological study revealed collagen deposition, fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis, and development of basement membrane in A. brasiliana group. The results of the present investigation revealed significant wound healing activity of MEAB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Alternanthera brasiliana improve cutaneous wound healing in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Oct;29(5):1443-1458. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00862-3. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34546478
-
Healing efficacy of methanol extract of leaves of Alternanthera brasiliana Kuntze in aged wound model.J Basic Clin Pharm. 2012 Sep;3(4):341-5. doi: 10.4103/0976-0105.105336. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2012. PMID: 24826048 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Alternanthera brasiliana (L) Kuntze on healing of dermal burn wound.Indian J Exp Biol. 2012 Jan;50(1):56-60. Indian J Exp Biol. 2012. PMID: 22279942
-
Wound healing activity of methanolic extract of leaves of Alternanthera brasiliana Kuntz using in vivo and in vitro model.Indian J Exp Biol. 2009 Dec;47(12):1001-5. Indian J Exp Biol. 2009. PMID: 20329705
-
In vivo wound-healing efficacy and antioxidant activity of Achyranthes aspera in experimental burns.Pharm Biol. 2012 Jul;50(7):892-9. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2011.642885. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Pharm Biol. 2012. PMID: 22480137
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Alternanthera brasiliana improve cutaneous wound healing in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Oct;29(5):1443-1458. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00862-3. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34546478
-
Biosynthesis, characterization, and evaluation of bioactivities of leaf extract-mediated biocompatible gold nanoparticles from Alternanthera bettzickiana.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2018 Jun 22;19:e00268. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2018.e00268. eCollection 2018 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2018. PMID: 29992102 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Plants from Latin America with Wound Healing Activity: Ethnomedicine, Phytochemistry, Preclinical and Clinical Studies-A Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;15(9):1095. doi: 10.3390/ph15091095. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genus Alternanthera: Phytochemical and Ethnopharmacological Perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 11;13:769111. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.769111. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35479320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological response of WAD sheep fed different combinations of Guinea grass and ensiled Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) O. Kuntze based diets: Intake, haematology and serum biochemical indices.Vet Anim Sci. 2021 Nov 20;14:100220. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2021.100220. eCollection 2021 Dec. Vet Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34877435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonard AL, Hanke CW. Second intention healing for intermediate and large postsurgical defects of the lip. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2007;57(5):832–835. - PubMed
-
- Rosen DJ, Patel MK, Freeman K, Weiss PR. A primary protocol for the management of ear keloids: results of excision combined with intraoperative and postoperative steroid injections. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2007;120(5):1395–1400. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A, Jain GK, Raghubir R. A time course study for the development of an immunocompromised wound model, using hydrocortisone. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 1999;41(4):183–187. - PubMed
-
- Cohen IK, Diegelmann RF, Johnson ML. Effect of corticosteroids on collagen synthesis. Surgery. 1977;82(1):15–20. - PubMed
-
- Barua CC, Talukdar A, Begum SA, et al. Wound healing activity of methanolic extract of leaves of Alternanthera brasiliana Kuntz using in vivo and in vitro model. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 2009;47(12):1001–1005. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
