Image microarrays derived from tissue microarrays (IMA-TMA): New resource for computer-aided diagnostic algorithm development
- PMID: 22934237
- PMCID: PMC3424658
- DOI: 10.4103/2153-3539.98168
Image microarrays derived from tissue microarrays (IMA-TMA): New resource for computer-aided diagnostic algorithm development
Abstract
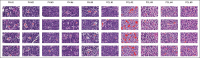
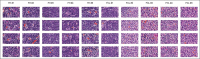
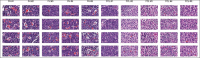
Background: Conventional tissue microarrays (TMAs) consist of cores of tissue inserted into a recipient paraffin block such that a tissue section on a single glass slide can contain numerous patient samples in a spatially structured pattern. Scanning TMAs into digital slides for subsequent analysis by computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) algorithms all offers the possibility of evaluating candidate algorithms against a near-complete repertoire of variable disease morphologies. This parallel interrogation approach simplifies the evaluation, validation, and comparison of such candidate algorithms. A recently developed digital tool, digital core (dCORE), and image microarray maker (iMAM) enables the capture of uniformly sized and resolution-matched images, with these representing key morphologic features and fields of view, aggregated into a single monolithic digital image file in an array format, which we define as an image microarray (IMA). We further define the TMA-IMA construct as IMA-based images derived from whole slide images of TMAs themselves.
Methods: Here we describe the first combined use of the previously described dCORE and iMAM tools, toward the goal of generating a higher-order image construct, with multiple TMA cores from multiple distinct conventional TMAs assembled as a single digital image montage. This image construct served as the basis of the carrying out of a massively parallel image analysis exercise, based on the use of the previously described spatially invariant vector quantization (SIVQ) algorithm.
Results: Multicase, multifield TMA-IMAs of follicular lymphoma and follicular hyperplasia were separately rendered, using the aforementioned tools. Each of these two IMAs contained a distinct spectrum of morphologic heterogeneity with respect to both tingible body macrophage (TBM) appearance and apoptotic body morphology. SIVQ-based pattern matching, with ring vectors selected to screen for either tingible body macrophages or apoptotic bodies, was subsequently carried out on the differing TMA-IMAs, with attainment of excellent discriminant classification between the two diagnostic classes.
Conclusion: The TMA-IMA construct enables and accelerates high-throughput multicase, multifield based image feature discovery and classification, thus simplifying the development, validation, and comparison of CAD algorithms in settings where the heterogeneity of diagnostic feature morphologic is a significant factor.
Keywords: CAD; IMA; SIVQ; TMA; WSI; dCORE; iMAM; image analysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Image microarrays (IMA): Digital pathology's missing tool.J Pathol Inform. 2011;2:47. doi: 10.4103/2153-3539.86829. Epub 2011 Oct 29. J Pathol Inform. 2011. PMID: 22200030 Free PMC article.
-
Robust gridding of TMAs after whole-slide imaging using template matching.Cytometry A. 2010 Dec;77(12):1169-76. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20949. Cytometry A. 2010. PMID: 20662092
-
Spatially Invariant Vector Quantization: A pattern matching algorithm for multiple classes of image subject matter including pathology.J Pathol Inform. 2011 Feb 26;2:13. doi: 10.4103/2153-3539.77175. J Pathol Inform. 2011. PMID: 21383936 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives in tissue microarrays.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2004 Sep;7(6):575-85. doi: 10.2174/1386207043328445. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2004. PMID: 15379629 Review.
-
Tissue microarrays: construction and use.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;980:13-28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-287-2_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23359147 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated prognostic pattern detection shows favourable diffuse pattern of FOXP3(+) Tregs in follicular lymphoma.Br J Cancer. 2015 Oct 20;113(8):1197-205. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.291. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26439683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avninder S, Ylaya K, Hewitt SM. Tissue microarray: a simple technology that has revolutionized research in pathology. J Postgrad Med. 2008;54:158–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

