The diversity of inducible and constitutively expressed erm(C) genes and association to different replicon types in staphylococci plasmids
- PMID: 22934240
- PMCID: PMC3429524
- DOI: 10.4161/mge.20109
The diversity of inducible and constitutively expressed erm(C) genes and association to different replicon types in staphylococci plasmids
Abstract
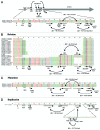
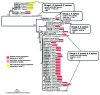
The aim of this study was to analyze the diversity of the macrolide resistance gene, erm(C) in relation to structural alterations affecting the gene expression. In addition, the association of erm(C) to mobile genetic elements (MGEs) in staphylococci mainly from Danish pigs was investigated. In total, 78 erythromycin-resistant isolates were screened for erm(C) by PCR. The erm(C) genes incl. the upstream regulatory region were sequenced and the expression types were characterized phenotypically (agar diffusion test) and genotypically (sequence analysis). Phylogenetic analysis of erm(C) was compared with structural alterations affecting the gene expression. Plasmids carrying erm(C) from seven selected isolates were fully or partially sequenced. Thirty-seven isolates were shown to be erm(C) positive and erm(C) from pigs were all constitutively expressed, mainly caused by different sized deletions (118, 111, 107, 70, 66, 16 and 3 bp) in the regulatory region. Duplication (63 bp) and substitutions were also found to cause a constitutive phenotype. Only one horse isolate had an inducible expression type. Phylogenetic analysis showed that structural alterations have happened in different erm(C) allele groups and not only in one group. Furthermore erm(C) was found mainly on plasmids (~2.4-8 kb) and gene sequence types correlated with plasmid replication (rep) gene types. One erm(C) type was linked to an IS257 element able to circularize. In conclusion, structural alterations giving rise to constitutive expression of erm(C) have happened several times in the evolution of erm(C). Interestingly, the diversity of erm(C) appears to be linked to the plasmid type or MGE carrying the gene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two different erm(C)-carrying plasmids in the same methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 isolate from a broiler farm.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Jul 16;171(3-4):382-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24553412
-
Molecular analysis of constitutively expressed erm(C) genes selected in vitro by incubation in the presence of the noninducers quinupristin, telithromycin, or ABT-773.Microb Drug Resist. 2002 Fall;8(3):171-7. doi: 10.1089/107662902760326878. Microb Drug Resist. 2002. PMID: 12363005
-
Molecular analysis of constitutively expressed erm(C) genes selected in vitro in the presence of the non-inducers pirlimycin, spiramycin and tylosin.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007 Jan;59(1):97-101. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl459. Epub 2006 Nov 3. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17085767
-
Presence of the tet(O) gene in erythromycin- and tetracycline-resistant strains of Streptococcus pyogenes and linkage with either the mef(A) or the erm(A) gene.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Sep;47(9):2844-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.9.2844-2849.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12936983 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile macrolide resistance genes in staphylococci.Plasmid. 2018 Sep;99:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 26. Plasmid. 2018. PMID: 29807043 Review.
Cited by
-
Epitranscriptional m6A modification of rRNA negatively impacts translation and host colonization in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jan 22;20(1):e1011968. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011968. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38252661 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional attenuation controls macrolide inducible efflux and resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and in other Gram-positive bacteria containing mef/mel(msr(D)) elements.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 19;10(2):e0116254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116254. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25695510 Free PMC article.
-
Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin resistance phenotypes and genotypes of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates from bovine mastitis.BMC Vet Res. 2015 Jul 25;11:168. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0492-8. BMC Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 26209340 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of Antibiotic Resistance Methyltransferase Correlates with mRNA Stability Independently of Ribosome Stalling.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Nov 21;60(12):7178-7188. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01806-16. Print 2016 Dec. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27645242 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing of macrolide resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A sequence type 416.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jul 25;20(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01909-1. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32711478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarestrup FM, Schwarz S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococci and Streptococci of Animal Origin. In: Aarestrup FM, ed. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial of Animal Origin. Washington: ASM, 2006; 187-212.
-
- Lodder G, Werckenthin C, Schwarz S, Dyke K. Molecular analysis of naturally occuring ermC-encoding plasmids in staphylococci isolated from animals with and without previous contact with macrolide/lincosamide antibiotics. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1997;18:7–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
