Widespread CD4+ T-cell reactivity to novel hTERT epitopes following vaccination of cancer patients with a single hTERT peptide GV1001
- PMID: 22934259
- PMCID: PMC3429571
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.20426
Widespread CD4+ T-cell reactivity to novel hTERT epitopes following vaccination of cancer patients with a single hTERT peptide GV1001
Abstract
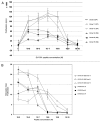
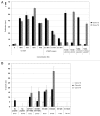
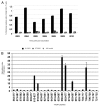
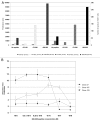
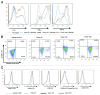
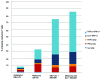
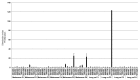
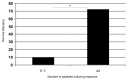
Understanding the basis of a successful clinical response after treatment with therapeutic cancer vaccines is essential for the development of more efficacious therapy. After vaccination with the single telomerase (hTERT) 16-mer peptide, GV1001, some patients experienced clinical responses and long-term survival. This study reports in-depth immunological analysis of the T-cell response against telomerase (hTERT) in clinically responding patients compared with clinical non-responders following vaccination with the single hTERT 16-mer peptide, GV1001. Extensive characterization of CD4+ T-cell clones specific for GV1001 generated from a lung cancer patient in complete remission after vaccination demonstrated a very broad immune response to this single peptide vaccine with differences in fine specificity, HLA restriction, affinity and function. Some CD4+ T-cell clones were cytotoxic against peptide-loaded target cells and also recognized processed recombinant hTERT protein. Furthermore, T-cell responses against several unrelated hTERT epitopes, some of which are novel, were detected, indicating extensive epitope spreading which was confirmed in other clinical responders. In contrast, patients responding immunologically, but not clinically, after vaccination did not display this intramolecular epitope spreading. Multifunctional CD4+ T-cell clones specific for novel hTERT epitopes were generated and shown to recognize a melanoma cell line. Pentamer analysis of T cells in peripheral blood also demonstrated the presence of an important CD8+ T-cell response recognizing an HLA-B7 epitope embedded in GV1001 not previously described. These results indicate that the highly diverse hTERT-specific T-cell response, integrating both T helper and CTL responses, is essential for tumor regression and the generation of long-term T-cell memory.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
