SALL4 is a key transcription regulator in normal human hematopoiesis
- PMID: 22934838
- PMCID: PMC3653586
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03888.x
SALL4 is a key transcription regulator in normal human hematopoiesis
Abstract
Background: Stem cell factor SALL4 is a zinc finger transcription factor. It plays vital roles in the maintenance of embryonic stem cell properties, functions as an oncogene in leukemia, and has been recently proposed to use for cord blood expansion. The mechanism(s) by which SALL4 functions in normal human hematopoiesis, including identification of its target genes, still need to be explored.
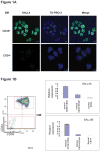
Study design and methods: Chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by microarray hybridization (ChIP-chip) was used for mapping SALL4 global gene targets in normal primary CD34+ cells. The results were then correlated with SALL4 functional studies in the CD34+ cells.
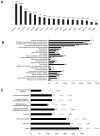
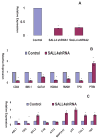
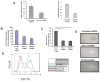
Results: More than 1000 potential SALL4 downstream target genes have been identified, and validation of binding by ChIP-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed for 5% of potential targets. These include genes that are involving in hematopoietic differentiation and self-renewal, such as HOXA9, RUNX1, CD34, and PTEN. Down regulation of SALL4 expression using small-hairpin RNA in these cells led to decreased in vitro myeloid colony-forming abilities and impaired in vivo engraftment. Furthermore, HOXA9 was identified to be a major SALL4 target in normal human hematopoiesis and the loss of either SALL4 or HOXA9 expression in CD34+ cells shared a similar phenotype.
Conclusion: Taken together, SALL4 is a key regulator in normal human hematopoiesis and the mechanism of its function is at least in part through the HOXA9. Future study will determine whether modulating the SALL4/HOXA9 pathway can be used in cellular therapy such as cord blood expansion and/or myeloid engraftment.
© 2012 American Association of Blood Banks.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author declares that she has no conflict of interest relevant to the manuscript submitted to Transfusion.
Figures


References
-
- Kohlhase J, Schubert L, Liebers M, et al. Mutations at the SALL4 locus on chromosome 20 result in a range of clinically overlapping phenotypes, including Okihiro syndrome, Holt-Oram syndrome, acro-renal-ocular syndrome, and patients previously reported to represent thalidomide embryopathy. J Med Genet. 2003;40:473–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

