Associations between kidney function and subclinical cardiac abnormalities in CKD
- PMID: 22935481
- PMCID: PMC3458463
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012020145
Associations between kidney function and subclinical cardiac abnormalities in CKD
Abstract
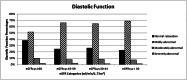
Heart failure is a common consequence of CKD, and it portends high risk for mortality. However, among patients without known heart failure, the associations of different stages of estimated GFR (eGFR) with changes in cardiac structure and function are not well described. Here, we performed a cross-sectional analysis to study these associations among 3487 participants of the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study. We estimated GFR using cystatin C. The prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) assessed by echocardiography was 32%, 48%, 57%, and 75% for eGFR categories ≥60, 45-59, 30-44, and <30 ml/min per 1.73 m(2), respectively. In fully adjusted multivariable analyses, subjects with eGFR levels of <30 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) had twofold higher odds of LVH (OR=2.20, 95% CI=1.40-3.40; P<0.001) relative to subjects with eGFR≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2). This reduction in kidney function also significantly associated with abnormal LV geometry but not diastolic or systolic dysfunction. An eGFR of 30-44 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) also significantly associated with LVH and abnormal LV geometry compared with eGFR≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2). In summary, in this large CKD cohort, reduced kidney function associated with abnormal cardiac structure. We did not detect significant associations between kidney function and systolic or diastolic function after adjusting for potential confounding variables.
Figures


Comment in
-
Chronic kidney disease: Reduced kidney function and abnormal cardiac structure.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 Nov;8(11):614. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.211. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22986359 No abstract available.
References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Kottgen A, Russell SD, Loehr LR, Crainiceanu CM, Rosamond WD, Chang PP, Chambless LE, Coresh J: Reduced kidney function as a risk factor for incident heart failure: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1307–1315, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Fried LF, Shlipak MG, Crump C, Bleyer AJ, Gottdiener JS, Kronmal RA, Kuller LH, Newman AB: Renal insufficiency as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in elderly individuals. J Am Coll Cardiol 41: 1364–1372, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Sarnak MJ, Katz R, Stehman-Breen CO, Fried LF, Jenny NS, Psaty BM, Newman AB, Siscovick D, Shlipak MG, Cardiovascular Health S, Cardiovascular Health Study : Cystatin C concentration as a risk factor for heart failure in older adults. Ann Intern Med 142: 497–505, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Shlipak MG, Katz R, Sarnak MJ, Fried LF, Newman AB, Stehman-Breen C, Seliger SL, Kestenbaum B, Psaty B, Tracy RP, Siscovick DS: Cystatin C and prognosis for cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in elderly persons without chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med 145: 237–246, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK093231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-029879./RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24DK92291/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-16500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK092291/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

