Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as skin carcinogens: comparison of benzo[a]pyrene, dibenzo[def,p]chrysene and three environmental mixtures in the FVB/N mouse
- PMID: 22935520
- PMCID: PMC3483092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.08.014
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as skin carcinogens: comparison of benzo[a]pyrene, dibenzo[def,p]chrysene and three environmental mixtures in the FVB/N mouse
Abstract
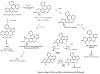
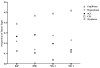
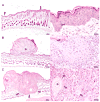
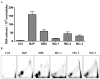
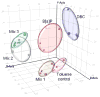
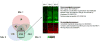
The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), was compared to dibenzo[def,p]chrysene (DBC) and combinations of three environmental PAH mixtures (coal tar, diesel particulate and cigarette smoke condensate) using a two stage, FVB/N mouse skin tumor model. DBC (4nmol) was most potent, reaching 100% tumor incidence with a shorter latency to tumor formation, less than 20 weeks of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) promotion compared to all other treatments. Multiplicity was 4 times greater than BaP (400 nmol). Both PAHs produced primarily papillomas followed by squamous cell carcinoma and carcinoma in situ. Diesel particulate extract (1 mg SRM 1650b; mix 1) did not differ from toluene controls and failed to elicit a carcinogenic response. Addition of coal tar extract (1 mg SRM 1597a; mix 2) produced a response similar to BaP. Further addition of 2 mg of cigarette smoke condensate (mix 3) did not alter the response with mix 2. PAH-DNA adducts measured in epidermis 12 h post initiation and analyzed by ³²P post-labeling, did not correlate with tumor incidence. PAH-dependent alteration in transcriptome of skin 12 h post initiation was assessed by microarray. Principal component analysis (sum of all treatments) of the 922 significantly altered genes (p<0.05), showed DBC and BaP to cluster distinct from PAH mixtures and each other. BaP and mixtures up-regulated phase 1 and phase 2 metabolizing enzymes while DBC did not. The carcinogenicity with DBC and two of the mixtures was much greater than would be predicted based on published Relative Potency Factors (RPFs).
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
None of the authors of this manuscript have any conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Figures


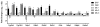
References
-
- Andrysik Z, Vondracek J, Marvanova S, Ciganek M, Neca J, Pencikova K, Mahadevan B, Topinka J, Baird WM, Kozubik A, Machala M. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor is the major toxic mode of action of an organic extract of a reference urban dust particulate matter mixture: the role of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mutat Res. 2011;714:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Arif JM, Smith WA, Gupta RC. DNA adduct formation and persistence in rat tissues following exposure to the mammary carcinogen dibenzo[a,l]pyrene. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20:1147–1150. - PubMed
-
- Arlt VM, Stiborova M, Henderson CJ, Thiemann M, Frei E, Aimova D, Singh R, Gamboa da Costa G, Schmitz OJ, Farmer PB, Wolf CR, Phillips DH. Metabolic activation of benzo[a]pyrene in vitro by hepatic cytochrome P450 contrasts with detoxification in vivo: experiments with hepatic cytochrome P450 reductase null mice. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:656–665. - PubMed
-
- ATSDR. Priority list of hazardous substances. 2011 http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/SPL/resources/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

