Role of phospholipid oxidation products in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 22935534
- PMCID: PMC3563283
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.256859
Role of phospholipid oxidation products in atherosclerosis
Abstract
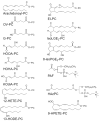
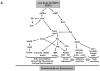
There is increasing clinical evidence that phospholipid oxidation products (Ox-PL) play a role in atherosclerosis. This review focuses on the mechanisms by which Ox-PL interact with endothelial cells, monocyte/macrophages, platelets, smooth muscle cells, and HDL to promote atherogenesis. In the past few years major progress has been made in identifying these mechanisms. It has been recognized that Ox-PL promote phenotypic changes in these cell types that have long-term consequences for the vessel wall. Individual Ox-PL responsible for specific cellular effects have been identified. A model of the configuration of bioactive truncated Ox-PL within membranes has been developed that demonstrates that the oxidized fatty acid moiety protrudes into the aqueous phase, rendering it accessible for receptor recognition. Receptors and signaling pathways for individual Ox-PL species are now determined and receptor independent signaling pathways identified. The effects of Ox-PL are mediated both by gene regulation and transcription independent processes. It has now become apparent that Ox-PL affects multiple genes and pathways, some of which are proatherogenic and some are protective. However, at concentrations that are likely present in the vessel wall in atherosclerotic lesions, the effects promote atherogenesis. There have also been new insights on enzymes that metabolize Ox-PL and the significance of these enzymes for atherosclerosis. With the knowledge we now have of the regulation and effects of Ox-PL in different vascular cell types, it should be possible to design experiments to test the role of specific Ox-PL on the development of atherosclerosis.
Figures





References
-
- Hahn BH, McMahon M. Atherosclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus: The role of altered lipids and of autoantibodies. Lupus. 2008;17:368–370. - PubMed
-
- Tsimikas S, Mallat Z, Talmud PJ, Kastelein JJ, Wareham NJ, Sandhu MS, Miller ER, Benessiano J, Tedgui A, Witztum JL, Khaw KT, Boekholdt SM. Oxidation-specific biomarkers, lipoprotein(a), and risk of fatal and nonfatal coronary events. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:946–955. - PubMed
-
- Choi SH, Chae A, Miller E, Messig M, Ntanios F, DeMaria AN, Nissen SE, Witztum JL, Tsimikas S. Relationship between biomarkers of oxidized low-density lipoprotein, statin therapy, quantitative coronary angiography, and atheroma: Volume observations from the reversal (reversal of atherosclerosis with aggressive lipid lowering) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:24–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1K99HL105577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL105577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL064731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL30568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL87823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T232HL69766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL058064/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL76259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL105577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

