AMP-activated protein kinase regulation and biological actions in the heart
- PMID: 22935535
- PMCID: PMC4397099
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.255505
AMP-activated protein kinase regulation and biological actions in the heart
Abstract
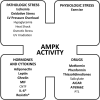
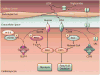
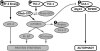
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a stress-activated kinase that functions as a cellular fuel gauge and master metabolic regulator. Recent investigation has elucidated novel molecular mechanisms of AMPK regulation and important biological actions of the AMPK pathway that are highly relevant to cardiovascular disease. Activation of the intrinsic AMPK pathway plays an important role in the myocardial response to ischemia, pressure overload, and heart failure. Pharmacological activation of AMPK shows promise as a therapeutic strategy in the treatment of heart disease. The purpose of this review is to assess how recent discoveries have extended and in some cases challenged existing paradigms, providing new insights into the regulation of AMPK, its diverse biological actions, and therapeutic potential in the heart.
Figures

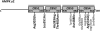
References
-
- Hardie DG, Carling D. The AMP-activated protein kinase--fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem. 1997;246:259–273. - PubMed
-
- Kemp BE, Stapleton D, Campbell DJ, Chen ZP, Murthy S, Walter M, Gupta A, Adams JJ, Katsis F, Van Denderen B, Jennings IG, Iseli T, Michell BJ, Witters LA. AMP-activated protein kinase, super metabolic regulator. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Yeh LA, Lee KH, Kim KH. Regulation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Regulation of phosphorylation and inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by the adenylate energy charge. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:2308–2314. - PubMed
-
- Carling D, Clarke P, Zammit V, Hardie D. Purification and characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase. Copurification of acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase activities. Eur J Biochem. 1989;186:129–136. - PubMed
-
- Kudo N, Barr AJ, Barr RL, Desai S, Lopaschuk GD. High rates of fatty acid oxidation during reperfusion of ischemic hearts are associated with a decrease in malonyl-CoA levels due to an increase in 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:17513–17520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

