Alternative Wnt pathways and receptors
- PMID: 22935904
- PMCID: PMC3475174
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007914
Alternative Wnt pathways and receptors
Abstract
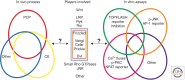
In addition to activating β-catenin/TCF transcriptional complexes, Wnt proteins can elicit a variety of other responses. These are often lumped together under the denominator "alternative" or "non-canonical" Wnt signaling, but they likely comprise distinct signaling events. In this article, I discuss how the use of different ligand and receptor combinations is thought to give rise to these alternative Wnt-signaling responses. Although many of the biochemical details remain to be resolved, it is evident that alternative Wnt signaling plays important roles in regulating tissue morphogenesis during embryonic development.
Figures

References
-
- Abu-Elmagd M, Garcia-Morales C, Wheeler GN 2006. Frizzled7 mediates canonical Wnt signaling in neural crest induction. Dev Biol 298: 285–298 - PubMed
-
- Adler PN 1992. The genetic control of tissue polarity in Drosophila. Bioessays 14: 735–741 - PubMed
-
- Afzal AR, Rajab A, Fenske CD, Oldridge M, Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E, Tuysuz B, Murday VA, Patton MA, Wilkie AO, et al. 2000. Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat Genet 25: 419–422 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
