Long term outcome of otosclerosis surgery
- PMID: 22936147
- PMCID: PMC9446357
- DOI: 10.1590/S1808-86942012000400021
Long term outcome of otosclerosis surgery
Abstract
The treatment of otosclerosis is eminently surgical. Good immediate results have been well documented when stapedotomy or stapedectomy are chosen.
Objectives: This study aims to assess long term audiometric performance after otosclerosis surgery.
Materials and methods: this retrospective study enrolled stapedotomy and partial stapedectomy patients seen at our service with proven hearing improvement after surgery. Forty-one patients (47 ears) accepted the invitation to be reassessed. Audiometry results before and immediately after surgery were compared.
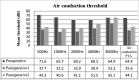
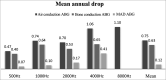
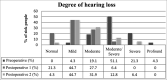
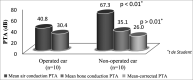
Results: the median late follow-up was 11 years. To this date, 49% of the patients had normal hearing or mild dysacusis. Preoperative, postoperative, and late postoperative bone and air pure tone averages were 64.4 and 27.0 dB, 35.6 and 22.3 dB, and 44.1 and 29.5 dB respectively.
Conclusion: Otosclerosis surgery offers good long term results. Despite the worsening of thresholds, the level of hypacusis ten years after surgery is lower than the levels observed before surgery.
Figures


References
-
- Thomas JP, Minovi A, Dazert S. Current aspects of etiology, diagnosis and therapy of otosclerosis. Otolaryngol Pol. 2011;65(3):162–170. - PubMed
-
- Merán Gil JL, Masgoret Palau E, Avilés Jurado FJ, Domènech Vadillo E, Flores Martín JC, Figuerola Massana E. Stapedotomy outcomes in the treatment of otosclerosis: our experience. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2008;59(9):448–454. - PubMed
-
- Chole RA, McKenna M. Pathophysiology of otosclerosis. Otol Neurotol. 2001;22(2):249–257. - PubMed
-
- Markou K, Goudakos J. An overview of the etiology of otosclerosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266(1):25–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

