High-fidelity promoter profiling reveals widespread alternative promoter usage and transposon-driven developmental gene expression
- PMID: 22936248
- PMCID: PMC3530677
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.139618.112
High-fidelity promoter profiling reveals widespread alternative promoter usage and transposon-driven developmental gene expression
Abstract
Many eukaryotic genes possess multiple alternative promoters with distinct expression specificities. Therefore, comprehensively annotating promoters and deciphering their individual regulatory dynamics is critical for gene expression profiling applications and for our understanding of regulatory complexity. We introduce RAMPAGE, a novel promoter activity profiling approach that combines extremely specific 5'-complete cDNA sequencing with an integrated data analysis workflow, to address the limitations of current techniques. RAMPAGE features a streamlined protocol for fast and easy generation of highly multiplexed sequencing libraries, offers very high transcription start site specificity, generates accurate and reproducible promoter expression measurements, and yields extensive transcript connectivity information through paired-end cDNA sequencing. We used RAMPAGE in a genome-wide study of promoter activity throughout 36 stages of the life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster, and describe here a comprehensive data set that represents the first available developmental time-course of promoter usage. We found that >40% of developmentally expressed genes have at least two promoters and that alternative promoters generally implement distinct regulatory programs. Transposable elements, long proposed to play a central role in the evolution of their host genomes through their ability to regulate gene expression, contribute at least 1300 promoters shaping the developmental transcriptome of D. melanogaster. Hundreds of these promoters drive the expression of annotated genes, and transposons often impart their own expression specificity upon the genes they regulate. These observations provide support for the theory that transposons may drive regulatory innovation through the distribution of stereotyped cis-regulatory modules throughout their host genomes.
Figures
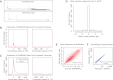
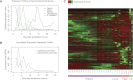
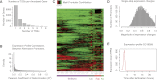



References
-
- Bejerano G, Lowe CB, Ahituv N, King B, Siepel A, Salama SR, Rubin EM, Kent WJ, Haussler D 2006. A distal enhancer and an ultraconserved exon are derived from a novel retroposon. Nature 441: 87–90 - PubMed
-
- Bourque G 2009. Transposable elements in gene regulation and in the evolution of vertebrate genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19: 607–612 - PubMed
-
- Britten RJ, Davidson EH 1969. Gene regulation for higher cells: A theory. Science 165: 349–357 - PubMed
-
- Bronner G, Taubert H, Jackle H 1995. Mesoderm-specific B104 expression in the Drosophila embryo is mediated by internal cis-acting elements of the transposon. Chromosoma 103: 669–675 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
