Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript is the neurotransmitter regulating the action of cholecystokinin and leptin on short-term satiety in rats
- PMID: 22936273
- PMCID: PMC3517666
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00231.2012
Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript is the neurotransmitter regulating the action of cholecystokinin and leptin on short-term satiety in rats
Retraction in
-
Retraction for Heldsinger et al., volume 303, 2012, p. G1042-G1051.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Feb 1;324(2):G157. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00231.2012_RET. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36649658 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
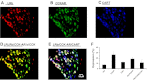
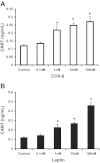
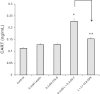
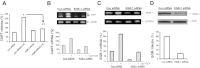
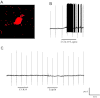
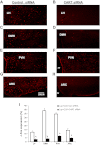
Vagal CCK-A receptors (CCKARs) and leptin receptors (LRbs) interact synergistically to mediate short-term satiety. Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptide is expressed by vagal afferent neurons. We sought to demonstrate that this neurotransmitter regulates CCK and leptin actions on short-term satiety. We also examined the signal transduction pathways responsible for mediating the CART release from the nodose ganglia (NG). ELISA studies coupled with gene silencing of NG neurons by RNA interference elucidated intracellular signaling pathways responsible for CCK/leptin-stimulated CART release. Feeding studies followed by gene silencing of CART in NG established the role of CART in mediating short-term satiety. Immunohistochemistry was performed on rat NG neurons to confirm colocalization of CCKARs and LRbs; 63% of these neurons contained CART. Coadministration of CCK-8 and leptin caused a 2.2-fold increase in CART release that was inhibited by CCK-OPE, a low-affinity CCKAR antagonist. Transfection of cultured NG neurons with steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) small-interfering RNA (siRNA) or STAT3 lentiviral short hairpin RNA inhibited CCK/leptin-stimulated CART release. Silencing the expression of the EGR-1 gene inhibited the CCK/leptin-stimulated CART release but had no effect on CCK/leptin-stimulated neuronal firing. Electroporation of NG with CART siRNA inhibited CCK/leptin stimulated c-Fos expression in rat hypothalamus. Feeding studies following electroporation of the NG with CART or STAT3 siRNA abolished the effects of CCK/leptin on short-term satiety. We conclude that the synergistic interaction of low-affinity vagal CCKARs and LRbs mediates CART release from the NG, and CART is the principal neurotransmitter mediating short-term satiety. CART release from the NG involves interaction between CCK/SRC/PI3K cascades and leptin/JAK2/PI3K/STAT3 signaling pathways.
Figures
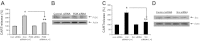
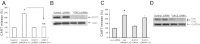
Similar articles
-
Synergistic interaction between leptin and cholecystokinin in the rat nodose ganglia is mediated by PI3K and STAT3 signaling pathways: implications for leptin as a regulator of short term satiety.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 1;286(13):11707-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.198945. Epub 2011 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21270124 Free PMC article.
-
Low-affinity CCK-A receptors are coexpressed with leptin receptors in rat nodose ganglia: implications for leptin as a regulator of short-term satiety.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):G217-27. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00356.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. Retraction in: Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Feb 1;324(2):G158. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00356.2010_RET. PMID: 21109591 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
KATP channels in the nodose ganglia mediate the orexigenic actions of ghrelin.J Physiol. 2015 Sep 1;593(17):3973-89. doi: 10.1113/JP270788. J Physiol. 2015. Retraction in: J Physiol. 2023 May;601(10):2049. doi: 10.1113/JP284696. PMID: 26174421 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Sensory signal transduction in the vagal primary afferent neurons.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(24):2554-63. doi: 10.2174/092986707782023334. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17979708 Review.
-
CCK-ergic mechanisms in sensory systems.Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2001;234:69-74. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11713983 Review.
Cited by
-
Levels of Cocaine- and Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript in Vagal Afferents in the Mouse Are Unaltered in Response to Metabolic Challenges.eNeuro. 2016 Oct 5;3(5):ENEURO.0174-16.2016. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0174-16.2016. eCollection 2016 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2016. PMID: 27822503 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling in rat brainstem via Gpr160 is required for the anorexigenic and antidipsogenic actions of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):R236-R249. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00096.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33206556 Free PMC article.
-
Satiety induced by bile acids is mediated via vagal afferent pathways.JCI Insight. 2020 Jul 23;5(14):e132400. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.132400. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32699194 Free PMC article.
-
CART in the regulation of appetite and energy homeostasis.Front Neurosci. 2014 Oct 13;8:313. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00313. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25352770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity of vagal afferent signaling in the gut.Medicina (Kaunas). 2017;53(2):73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.medici.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Medicina (Kaunas). 2017. PMID: 28454890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aja S, Sahandy S, Ladenheim EE, Schwartz GJ, Moran TH. Intracerebroventricular CART peptide reduces food intake and alters motor behavior at a hindbrain site. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281: R1862–R1867, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Banks AS, Davis SM, Bates SH, Myers MG., Jr Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 275: 14563–14572, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

