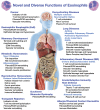
The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease
- PMID: 22936660
- PMCID: PMC3496950
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-330845
The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease
Abstract
Surprisingly, the role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease is often summarized by clinicians and basic research scientists as a pervasive consensus opinion first learned in medical/graduate school. Eosinophils are rare white blood cells whose activities are primarily destructive and are only relevant in parasitic infections and asthma. However, is this consensus correct? This review argues that the wealth of available studies investigating the role(s) of eosinophils in both health and disease demonstrates that the activities of these granulocytes are far more expansive and complex than previously appreciated. In turn, this greater understanding has led to the realization that eosinophils have significant contributory roles in a wide range of diseases. Furthermore, published studies even implicate eosinophil-mediated activities in otherwise healthy persons. We suggest that the collective reports in the literature showing a role for eosinophils in an ever-increasing number of novel settings highlight the true complexity and importance of this granulocyte. Indeed, discussions of eosinophils are no longer simple and more often than not now begin with the question/statement "Did you know …?"
Figures
References
-
- Meeusen EN, Balic A. Do eosinophils have a role in the killing of helminth parasites? Parasitol Today. 2000;16(3):95–101. - PubMed
-
- Gleich GJ. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990;85(2):422–436. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen EA, Taranova AG, Lee NA, Lee JJ. Eosinophils: singularly destructive effector cells or purveyors of immunoregulation? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(6):1313–1320. - PubMed
-
- Giembycz MA, Lindsay MA. Pharmacology of the eosinophil. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51(2):213–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources