Antitumor T-cell responses contribute to the effects of dasatinib on c-KIT mutant murine mastocytoma and are potentiated by anti-OX40
- PMID: 22936666
- PMCID: PMC3512233
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-407163
Antitumor T-cell responses contribute to the effects of dasatinib on c-KIT mutant murine mastocytoma and are potentiated by anti-OX40
Abstract
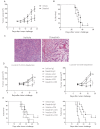
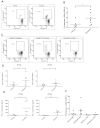
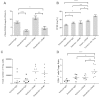
Targeted and immune-based therapies are thought to eradicate cancer cells by different mechanisms, and these approaches could possibly complement each other when used in combination. In this study, we report that the in vivo antitumor effects of the c-KIT inhibitor, dasatinib, on the c-KIT mutant P815 mastocytoma tumor were substantially dependent on T cell-mediated immunity. We found that dasatinib treatment significantly decreased levels of Tregs while specifically enhancing tumor antigen-specific T-cell responses. We sought to further enhance this therapy with the addition of anti-OX40 antibody, which is known to provide a potent costimulatory signal to T cells. The combination of dasatinib and anti-OX40 antibody resulted in substantially better therapeutic efficacy compared with either drug alone, and this was associated with enhanced accumulation of tumor antigen-specific T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, the combination regimen inhibited the function of Tregs and also resulted in significantly up-regulated expression of the IFN-γ-induced chemokines CXCL9, 10, and 11 in the tumor microenvironment, which provides a feasible mechanism for the enhanced intratumoral CTL infiltration. These studies delineate a strategy by which targeted therapy and immunotherapy may be combined to achieve superior antitumor responses in cancer patients.
Figures




Comment in
-
Immunobiology. Combined targeted and immunotherapy: the future of personalized medicine.Blood. 2012 Nov 29;120(23):4454-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-455105. Blood. 2012. PMID: 23197581
References
-
- Bickenbach K, Wilcox R, Veerapong J, et al. A review of resistance patterns and phenotypic changes in gastrointestinal stromal tumors following imatinib mesylate therapy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007;11(6):758–766. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI, Atkins MB. Resistance to targeted therapy in renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(10):992–1000. - PubMed
-
- Smalley KS. PLX-4032, a small-molecule B-Raf inhibitor for the potential treatment of malignant melanoma. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;11(6):699–706. - PubMed
-
- Lennartsson J, Ronnstrand L. The stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit as a drug target in cancer. Current Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6(1):65–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

