Synthesis of methylphosphonic acid by marine microbes: a source for methane in the aerobic ocean
- PMID: 22936780
- PMCID: PMC3466329
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1219875
Synthesis of methylphosphonic acid by marine microbes: a source for methane in the aerobic ocean
Abstract
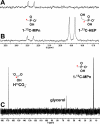
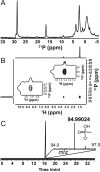
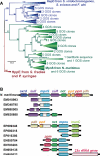
Relative to the atmosphere, much of the aerobic ocean is supersaturated with methane; however, the source of this important greenhouse gas remains enigmatic. Catabolism of methylphosphonic acid by phosphorus-starved marine microbes, with concomitant release of methane, has been suggested to explain this phenomenon, yet methylphosphonate is not a known natural product, nor has it been detected in natural systems. Further, its synthesis from known natural products would require unknown biochemistry. Here we show that the marine archaeon Nitrosopumilus maritimus encodes a pathway for methylphosphonate biosynthesis and that it produces cell-associated methylphosphonate esters. The abundance of a key gene in this pathway in metagenomic data sets suggests that methylphosphonate biosynthesis is relatively common in marine microbes, providing a plausible explanation for the methane paradox.
Figures
References
-
- Rogers JE, Whitman WB, editors. Microbial production and consumption of greenhouse gases : methane, nitrogen oxides, and halomethanes. American Society for Microbiology; Washington, D.C.: 1991.
-
- Karl DM, et al. Nat. Geosci. 2008;1:473.
-
- Reeburgh WS. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:486. - PubMed
-
- Daughton CG, Cook AM, Alexander M. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1979;5:91.
-
- Martinez A, Tyson GW, DeLong EF. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;12:222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

