The TT genotype of the STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism is associated with high disease activity and disability in patients with early arthritis
- PMID: 22937072
- PMCID: PMC3427144
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043661
The TT genotype of the STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism is associated with high disease activity and disability in patients with early arthritis
Abstract
Background: The number of copies of the HLA-DRB1 shared epitope, and the minor alleles of the STAT4 rs7574865 and the PTPN22 rs2476601 polymorphisms have all been linked with an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. In the present study, we investigated the effects of these genetic variants on disease activity and disability in patients with early arthritis.
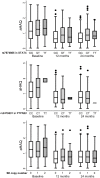
Methodology and results: We studied 640 patients with early arthritis (76% women; median age, 52 years), recording disease-related variables every 6 months during a 2-year follow-up. HLA-DRB1 alleles were determined by PCR-SSO, while rs7574865 and rs2476601 were genotyped with the Taqman 5' allelic discrimination assay. Multivariate analysis was performed using generalized estimating equations for repeated measures. After adjusting for confounding variables such as gender, age and ACPA, the TT genotype of rs7574865 in STAT4 was associated with increased disease activity (DAS28) as compared with the GG genotype (β coefficient [95% confidence interval] = 0.42 [0.01-0.83], p = 0.044). Conversely, the presence of the T allele of rs2476601 in PTPN22 was associated with diminished disease activity during follow-up in a dose-dependent manner (CT genotype = -0.27 [-0.56- -0.01], p = 0.042; TT genotype = -0.68 [-1.64- -0.27], p = 0.162). After adjustment for gender, age and disease activity, homozygosity for the T allele of rs7574865 in STAT4 was associated with greater disability as compared with the GG genotype.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that patients with early arthritis who are homozygous for the T allele of rs7574865 in STAT4 may develop a more severe form of the disease with increased disease activity and disability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- MacGregor AJ, Snieder H, Rigby AS, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, et al. (2000) Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum 43: 30–37. - PubMed
-
- Orozco G, Rueda B, Martin J (2006) Genetic basis of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother 60: 656–662. - PubMed
-
- Orozco G, Alizadeh BZ, Delgado-Vega AM, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Balsa A, et al. (2008) Association of STAT4 with rheumatoid arthritis: a replication study in three European populations. Arthritis Rheum 58: 1974–1980. - PubMed
-
- Orozco G, Sanchez E, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Lopez-Nevot MA, Torres B, et al. (2005) Association of a functional single-nucleotide polymorphism of PTPN22, encoding lymphoid protein phosphatase, with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 52: 219–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

