Enantioselective cytotoxicity profile of o,p'-DDT in PC 12 cells
- PMID: 22937105
- PMCID: PMC3427172
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043823
Enantioselective cytotoxicity profile of o,p'-DDT in PC 12 cells
Abstract
Background: The continued uses of dichlordiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) for indoor vector control in some developing countries have recently fueled intensive debates toward the global ban of this persistent legacy contaminant. Current approaches for ecological and health risk assessment has ignored the chiral nature of DDT. In this study by employing an array of cytotoxicity related endpoints, we investigated the enantioselective cytotoxicity of o,p'-DDT.
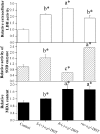
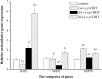
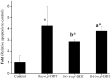
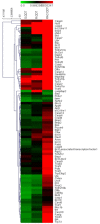
Principal findings: we demonstrated for the first time that R-(-)-o,p'-DDT caused more neuron cell death by inducing more severe oxidative stress, which selectively imbalanced the transcription of stress-related genes (SOD1, SOD2, HSP70) and enzyme (superoxide dismutase and lactate dehydrogenase) activities, and greater cellular apoptosis compared to its enantiomer S-(+)-o,p'-DDT at the level comparable to malaria area exposure (parts per million). We further elucidated enantioselective modes of action using microarray combined with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The enantioselective apoptosis might involve three signaling pathways via caspase 3, tumor protein 53 (p53) and NF(k)B.
Conclusions: Based on DDT stereochemistry and results reported for other chiral pesticides, our results pointed to the same directional enantioselectivity of chiral DDT toward mammalian cells. We proposed that risk assessment on DDT should consider the enantiomer ratio and enantioselectivities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enantioselective induction of cytotoxicity by o,p'-DDD in PC12 cells: implications of chirality in risk assessment of POPs metabolites.Environ Sci Technol. 2013 Apr 16;47(8):3909-17. doi: 10.1021/es3049306. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Environ Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 23485034
-
Enantiomer-specific activity of o,p'-DDT with the human estrogen receptor.Toxicol Lett. 2001 Dec 15;125(1-3):75-81. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(01)00410-6. Toxicol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11701225
-
Enantioselective estrogenicity of o,p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane in the MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell line.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2009 Jan;28(1):1-8. doi: 10.1897/08-055.1. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2009. PMID: 18700809
-
Enantioselective Effects of o,p'-DDT on Cell Invasion and Adhesion of Breast Cancer Cells: Chirality in Cancer Development.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Aug 18;49(16):10028-37. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b02147. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26225806
-
Enantiomer-specific profenofos-induced cytotoxicity and DNA damage mediated by oxidative stress in rat adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells.J Appl Toxicol. 2014 Feb;34(2):166-75. doi: 10.1002/jat.2847. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Appl Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 23495063
Cited by
-
Comparative neurotoxicity screening in human iPSC-derived neural stem cells, neurons and astrocytes.Brain Res. 2016 May 1;1638(Pt A):57-73. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.07.048. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26254731 Free PMC article.
-
Protective efficacy of vitamins C and E on p,p'-DDT-induced cytotoxicity via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and NF-κB/FasL pathway.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e113257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113257. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25464339 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Flumethrin Pyrethroid on SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells: Apoptosis Associated with Oxidative Stress.Toxics. 2022 Mar 7;10(3):131. doi: 10.3390/toxics10030131. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35324756 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Environmental Risk Factors on Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Neuroinflammation, Protein Misfolding, and Oxidative Stress in the Etiopathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10808. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810808. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leber ER, Benya TJ (1994) Chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. Patty’s Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. Vol. 2, Part B, New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc; 1503–1506.
-
- Stemmler I, Lammel G (2009) Cycling of DDT in the global environment 1950–2002: World ocean returns the pollutant. Geophys Res Lett 36: L24602–L24606.
-
- UNEP. Stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants (POPs). UNEP/Chemicals/2002/9. 2002, Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme.
-
- van Dyk JC, Bouwman H, Barnhoorn IE, Bornman MS (2010) DDT contamination from indoor residual spraying for malaria control. Sci Total Environ 408: 2745–2752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

