High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in pregnant women: a national cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 22937114
- PMCID: PMC3427250
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043868
High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in pregnant women: a national cross-sectional survey
Abstract
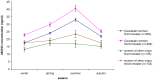
An increasing number of studies suggest that vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy is associated with multiple adverse health outcomes in mothers, neonates and children. There are no representative country data available on vitamin D status of pregnant women in Europe. The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Belgian pregnant women and to assess the determinants of vitamin D status in the first and third trimester of pregnancy. The women were selected via a multi-stage proportionate-to-size sampling design. Blood samples were collected and a questionnaire was completed face-to-face. 55 obstetric clinics were randomly selected and 1311 pregnant women participated in the study. The median serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25-(OH)D] concentration was significantly lower in the first trimester (20.4 ng/ml) than in third trimester (22.7 ng/ml). Of all women, 74.1% (95%CI = 71.8-76.5%) were vitamin D insufficient (25-(OH)D <30 ng/ml), 44.6% (95%CI = 41.9-47.3%) were vitamin D deficient (25-(OH)D <20 ng/ml), while 12.1% (95%CI = 10.3-13.8%) were severely vitamin D deficient (25-(OH)D <10 ng/ml). Of all women included, 62.0% reported taking vitamin D-containing multivitamins, of which only 24.2% started taking those before pregnancy. The risk of vitamin D deficiency (25-(OH)D <20 ng/ml) was significantly higher for less educated women and women who reported not going on holidays to sunny climates. The risk of severe vitamin D deficiency (25-(OH)D <10 ng/ml) decreased for women who reported alcohol consumption during pregnancy, decreased with more frequent use of sunscreen lotion and increased for smokers and women who reported preference for shadow. In conclusion, vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent among pregnant women in Belgium and this raises concerns about the health consequences for the mother and the offspring. A targeted screening strategy to detect and treat women at high risk of severe vitamin D deficiency is needed in Belgium and in Europe.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Valimaki VV, Alfthan H, Lehmuskallio E, Loyttyniemi E, Sahi T, et al. (2004) Vitamin D status as a determinant of peak bone mass in young Finnish men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89: 76–80. - PubMed
-
- Ooms ME, Roos JC, Bezemer PD, van der Vijgh WJ, Bouter LM, et al. (1995) Prevention of bone loss by vitamin D supplementation in elderly women: a randomized double-blind trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80: 1052–1058. - PubMed
-
- Lips P, van Schoor NM (2011) The effect of vitamin D on bone and osteoporosis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 25: 585–591. - PubMed
-
- Jackson C, Gaugris S, Sen SS, Hosking D (2007) The effect of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) on the risk of fall and fracture: a meta-analysis. QJM 100: 185–192. - PubMed
-
- Pettifor JM, Prentice A (2011) The role of vitamin D in paediatric bone health. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 25: 573–584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

