Is inflammation a mitochondrial dysfunction-dependent event in fibromyalgia?
- PMID: 22938055
- PMCID: PMC3555092
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2012.4892
Is inflammation a mitochondrial dysfunction-dependent event in fibromyalgia?
Abstract
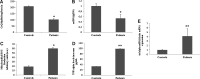
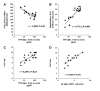
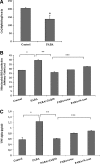
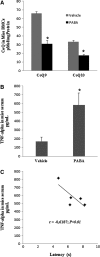
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a complex disorder that affects up to 5% of the general population worldwide. Both mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation have been implicated in the pathophysiology of FM. We have investigated the possible relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation in FM. We studied 30 women diagnosed with FM and 20 healthy women. Blood mononuclear cells (BMCs) from FM patients showed reduced level of coenzyme Q₁₀ (CoQ₁₀) and mtDNA contents and high level of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and transcript levels. A significant negative correlation between CoQ₁₀ and TNF-alpha levels (r=-0.588; p<0.01), and a positive correlation between ROS and TNF-alpha levels (r=0.791; p<0.001) were observed accompanied by a significant correlation of visual analogical scale with serum TNF-alpha and transcript levels (r=0.4507; p<0.05 and r=0.7089; p<0.001, respectively). TNF-alpha release was observed in an in vitro (BMCs) and in vivo (mice) CoQ₁₀ deficiency model. Oral CoQ₁₀ supplementation restored biochemical parameters and induced a significant improvement in clinical symptoms (p<0.001). These results lead to the hypothesis that inflammation could be a mitochondrial dysfunction-dependent event implicated in the pathophysiology of FM in several patients indicating at mitochondria as a possible new therapeutic target.
Figures
References
-
- Cloonan SM. Choi AM. Mitochondria: commanders of innate immunity and disease? Curr Opin Immunol. 2012;24:32–40. - PubMed
-
- Ozgocmen S. Ozyurt H. Sogut S. Akyol O. Current concepts in the pathophysiology of fibromyalgia: the potential role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:585–597. - PubMed
-
- Rüster M. Franke S. Späth M. Pongratz DE. Stein G. Hein GE. Detection of elevated N epsilon-carboxymethyllysine levels in muscular tissue and in serum of patients with fibromyalgia. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005;34:460–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

