Reconstruction of fetal brain MRI with intensity matching and complete outlier removal
- PMID: 22939612
- PMCID: PMC4067058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2012.07.004
Reconstruction of fetal brain MRI with intensity matching and complete outlier removal
Abstract
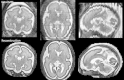
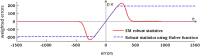
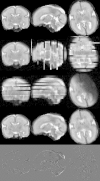
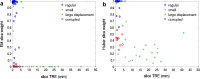
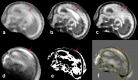
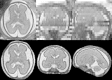
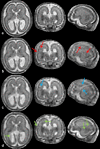
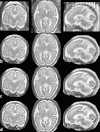
We propose a method for the reconstruction of volumetric fetal MRI from 2D slices, comprising super-resolution reconstruction of the volume interleaved with slice-to-volume registration to correct for the motion. The method incorporates novel intensity matching of acquired 2D slices and robust statistics which completely excludes identified misregistered or corrupted voxels and slices. The reconstruction method is applied to motion-corrupted data simulated from MRI of a preterm neonate, as well as 10 clinically acquired thick-slice fetal MRI scans and three scan-sequence optimized thin-slice fetal datasets. The proposed method produced high quality reconstruction results from all the datasets to which it was applied. Quantitative analysis performed on simulated and clinical data shows that both intensity matching and robust statistics result in statistically significant improvement of super-resolution reconstruction. The proposed novel EM-based robust statistics also improves the reconstruction when compared to previously proposed Huber robust statistics. The best results are obtained when thin-slice data and the correct approximation of the point spread function is used. This paper addresses the need for a comprehensive reconstruction algorithm of 3D fetal MRI, so far lacking in the scientific literature.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





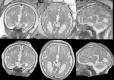
References
-
- Ashburner J., Friston K.J. Unified segmentation. NeuroImage. 2005;26:839–851. - PubMed
-
- Bertelsen, A., Aljabar, P., Xue, H., Srinivasan, L., Hayat, T., Allsop, J., Rueckert, D., Rutherford, M.R., Hajnal, J.V., 2009. Improved slice to volume reconstruction of the fetal brain for automated cortex segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Society for, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, p. 3437.
-
- Charbonnier P., Blanc-Feraud L., Aubert G., Barlaud M. Deterministic edge-preserving regularization in computed imaging. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 1997;6:298–311. - PubMed
-
- Clouchoux C., Kudelski D., Gholipour A., Warfield S., Viseur S., Bouyssi-Kobar M., Mari J.L., Evans A., du Plessis A., Limperopoulos C. Quantitative in vivo MRI measurement of cortical development in the fetus. Brain Structure and Function. 2012;217:127–139. - PubMed
-
- Damodaram M., Story L., Allsop J., McGuinness A., Patel A., Kumar S., Rutherford M. 3-dimensional MR reconstruction and brain volumetry in IUGR fetuses. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics. 2009;107:S463–S464. (Abstracts of XIX FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics)
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

