Single-stranded RNAs use RNAi to potently and allele-selectively inhibit mutant huntingtin expression
- PMID: 22939619
- PMCID: PMC3444165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.002
Single-stranded RNAs use RNAi to potently and allele-selectively inhibit mutant huntingtin expression
Abstract
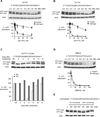
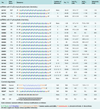
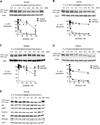
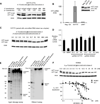
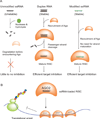
Mutant huntingtin (HTT) protein causes Huntington disease (HD), an incurable neurological disorder. Silencing mutant HTT using nucleic acids would eliminate the root cause of HD. Developing nucleic acid drugs is challenging, and an ideal clinical approach to gene silencing would combine the simplicity of single-stranded antisense oligonucleotides with the efficiency of RNAi. Here, we describe RNAi by single-stranded siRNAs (ss-siRNAs). ss-siRNAs are potent (>100-fold more than unmodified RNA) and allele-selective (>30-fold) inhibitors of mutant HTT expression in cells derived from HD patients. Strategic placement of mismatched bases mimics micro-RNA recognition and optimizes discrimination between mutant and wild-type alleles. ss-siRNAs require Argonaute protein and function through the RNAi pathway. Intraventricular infusion of ss-siRNA produced selective silencing of the mutant HTT allele throughout the brain in a mouse HD model. These data demonstrate that chemically modified ss-siRNAs function through the RNAi pathway and provide allele-selective compounds for clinical development.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
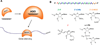

Comment in
-
Singles engage the RNA interference pathway.Cell. 2012 Aug 31;150(5):873-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.008. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22939614
References
-
- Braasch DA, Jensen S, Liu Y, Arar K, White MA, Corey DR. RNA interference in mammalian cells by chemically modified RNA. Biochemistry. 2003;42:7967–7975. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JB, Warby SC, Southwell AL, Doty CN, Greenlee S, Skotte N, Hung G, Bennett CF, Freier SM, Hayden MR. Potent and selective antisense oligonucleotides targeting single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the Huntington disease gene / allele-specific silencing of mutant huntingtin. Mol Ther. 2011;19:2178–2185. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

