Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and allergic disease
- PMID: 22939755
- PMCID: PMC3462264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.010
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and allergic disease
Abstract
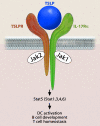
The importance of the epithelium in initiating and controlling immune responses is becoming more appreciated. For example, allergen contact first occurs at mucosal sites exposed to the external environment, such as the skin, airways, and gastrointestinal tract. This exposure leads to the production of a variety of cytokines and chemokines that are involved in driving allergic inflammatory responses. One such product is thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). Recent studies in both human subjects and murine models have implicated TSLP in the development and progression of allergic diseases. This review will highlight recent advances in the understanding of the role of TSLP in these inflammatory diseases. Importantly, these insights into TSLP's multifaceted role could potentially allow for novel therapeutic manipulations of these disorders.
Copyright © 2012 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Reche PA, Soumelis V, Gorman DM, Clifford T, Liu M, Travis M, et al. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates myeloid cells. J Immunol. 2001;167(1):336–43. - PubMed
-
- Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward G, Homey B, et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(7):673–80. - PubMed
-
- Ying S, O'Connor B, Ratoff J, Meng Q, Mallett K, Cousins D, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting chemokines and disease severity. J Immunol. 2005;174(12):8183–90. - PubMed
-
- Mou Z, Xia J, Tan Y, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhou B, et al. Overexpression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergic rhinitis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009;129(3):297–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

