Osteocyte control of osteoclastogenesis
- PMID: 22939943
- PMCID: PMC3538915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.08.121
Osteocyte control of osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
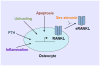
Multiple lines of evidence support the idea that osteocytes act as mechanosensors in bone and that they control bone formation, in part, by expressing the Wnt antagonist sclerostin. However, the role of osteocytes in the control of bone resorption has been less clear. Recent studies have demonstrated that osteocytes are the major source of the cytokine RANKL involved in osteoclast formation in cancellous bone. The goal of this review is to discuss these and other studies that reveal mechanisms whereby osteocytes control osteoclast formation and thus bone resorption.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL, Timms E, Capparelli C, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999;397:315–23. - PubMed
-
- Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Luthy R, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997;89:309–19. - PubMed
-
- Balemans W, Ebeling M, Patel N, Van HE, Olson P, Dioszegi M, et al. Increased bone density in sclerosteosis is due to the deficiency of a novel secreted protein (SOST) Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:537–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources