MicroRNA 16 modulates epithelial sodium channel in human alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 22940131
- PMCID: PMC3536022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.063
MicroRNA 16 modulates epithelial sodium channel in human alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
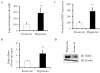
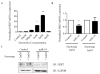
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a devastating disease characterized by pulmonary edema. Removal of edema from the air spaces of lung is a critical function of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in ALI. The molecular mechanisms behind resolution of pulmonary edema are incompletely understood. MicroRNA's (miRNA) are crucial gene regulators and are dysregulated in various diseases including ALI. Recent studies suggest that microRNA-16 (miR-16) targets serotonin transporter (SERT) involved in the serotonin (5-HT) transmitter system. Alterations in serotonin levels have been reported in various pulmonary diseases. However, the role of miR-16 on its target SERT, and ENaC, a key ion channel involved in the resolution of pulmonary edema, have not been studied. In the present study, the expression patterns of miR-16, SERT, ENaC and serotonin were investigated in mice exposed to room air and hyperoxia. The effects of miR-16 overexpression on ENaC, SERT, TGF-β and Nedd4 in human alveolar epithelial cells were analyzed. miR-16 and ENaC were downregulated in mice exposed to hyperoxia. miR-16 downregulation in mouse lung was correlated with an increase in SERT expression and pulmonary edema. Overexpression of miR-16 in human alveolar epithelial cells (A549) suppressed SERT and increased ENaCβ levels when compared to control-vector transfected cells. In addition, miR-16 over expression suppressed TGFβ release, a critical inhibitor of ENaC. Interestingly Nedd4, a negative regulator of ENaC remained unaltered in miR-16 over expressed A549 cells when compared to controls. Taken together, our data suggests that miR-16 upregulates ENaC, a major sodium channel involved in resolution of pulmonary edema in ALI.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
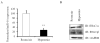

Similar articles
-
Regulation of ENaC-mediated alveolar fluid clearance by insulin via PI3K/Akt pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2012 Mar 30;13(1):29. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-29. Respir Res. 2012. PMID: 22458687 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin1 stimulates alveolar fluid clearance through the alveolar epithelial sodium channel Na,K-ATPase via the ALX/PI3K/Nedd4-2 pathway.Lab Invest. 2017 May;97(5):543-554. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.150. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Lab Invest. 2017. PMID: 28218740
-
Hypoxia-induced inhibition of epithelial Na(+) channels in the lung. Role of Nedd4-2 and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 Mar;50(3):526-37. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0518OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24093724
-
NEDD4-2 (NEDD4L): the ubiquitin ligase for multiple membrane proteins.Gene. 2015 Feb 15;557(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.051. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25433090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of ENaC-mediated sodium transport in alveolar fluid clearance using genetically-engineered mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;25(1):63-70. doi: 10.1159/000272051. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20054145 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of microRNAs in lung development and pulmonary diseases.Pulm Circ. 2013 Apr;3(2):315-28. doi: 10.4103/2045-8932.114758. Pulm Circ. 2013. PMID: 24015331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A MicroRNA Cluster miR-23-24-27 Is Upregulated by Aldosterone in the Distal Kidney Nephron Where it Alters Sodium Transport.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Jun;232(6):1306-1317. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25599. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27636893 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in mucosal inflammation.J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Sep;95(9):935-949. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1568-7. Epub 2017 Jul 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28726085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-338-5p modulates pulmonary hypertension-like injuries caused by SO2, NO2 and PM2.5 co-exposure through targeting the HIF-1α/Fhl-1 pathway.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2016 Sep 9;5(6):1548-1560. doi: 10.1039/c6tx00257a. eCollection 2016 Nov 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2016. PMID: 30090456 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages: Their role, activation and polarization in pulmonary diseases.Immunobiology. 2018 Apr-May;223(4-5):383-396. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 12. Immunobiology. 2018. PMID: 29146235 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

