Effects of gonadal hormones on the peripheral cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) system under a myositis condition in rats
- PMID: 22940464
- PMCID: PMC3578305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.07.037
Effects of gonadal hormones on the peripheral cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) system under a myositis condition in rats
Abstract
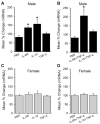
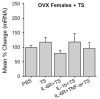
In this study, we assessed the effects of peripherally administered cannabinoids in an orofacial myositis model, and the role of sex hormones in cannabinoid receptor (CBR) expression in trigeminal ganglia (TG). Peripherally administered arachidonylcyclopropylamide (ACPA), a specific CB1R agonist, significantly attenuated complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced mechanical hypersensitivity in the masseter muscle in male rats. The ACPA effect was blocked by a local administration of AM251, a specific CB1R antagonist, but not by AM630, a specific CB2R antagonist. In female rats, a 30-fold higher dose of ACPA was required to produce a moderate reduction in mechanical hypersensitivity. CFA injected in masseter muscle significantly upregulated CB1R mRNA expression in TG in male, but not in female, rats. There was a close correlation between the CB1R mRNA levels in TG and the antihyperalgesic effect of ACPA. Interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, which are elevated in the muscle tissue following CFA treatment, induced a significant upregulation of CB1R mRNA expression in TG from male rats. The upregulation of CB1R was prevented in TG cultures from orchidectomized male rats, which was restored by the application of testosterone. The cytokines did not alter the CB1R mRNA level in TG from intact as well as ovariectomized female rats. Neither estradiol supplement nor estrogen receptor blockade had any effects on CB1R expression. These data indicate that testosterone, but not estradiol, is required for the regulation of CB1Rs in TG under inflammatory conditions, which provide explanations for the sex differences in the antihyperalgesic effects of peripherally administered cannabinoids.
Copyright © 2012 International Association for the Study of Pain. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

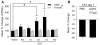
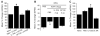
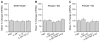

Similar articles
-
Effect of Testosterone on TRPV1 Expression in a Model of Orofacial Myositis Pain in the Rat.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jan;64(1):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-1009-7. Epub 2017 Dec 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29209900
-
Sex differences in μ-opioid receptor expression in trigeminal ganglia under a myositis condition in rats.Eur J Pain. 2014 Feb;18(2):151-61. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00352.x. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Eur J Pain. 2014. PMID: 23801566 Free PMC article.
-
A peripherally restricted cannabinoid receptor agonist produces robust anti-nociceptive effects in rodent models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain.Pain. 2010 Nov;151(2):337-344. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.07.019. Epub 2010 Aug 8. Pain. 2010. PMID: 20696525
-
Cannabinoids in pain management: CB1, CB2 and non-classic receptor ligands.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Aug;23(8):1123-40. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.918603. Epub 2014 May 16. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24836296 Review.
-
Modern approaches to the development of synthetic cannabinoid receptor probes.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021 Apr;203:173119. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173119. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021. PMID: 33508249 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined non-psychoactive Cannabis components cannabidiol and β-caryophyllene reduce chronic pain via CB1 interaction in a rat spinal cord injury model.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 13;18(3):e0282920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282920. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36913400 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences and the endocannabinoid system in pain.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021 Mar;202:173107. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173107. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021. PMID: 33444598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Testosterone on TRPV1 Expression in a Model of Orofacial Myositis Pain in the Rat.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jan;64(1):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-1009-7. Epub 2017 Dec 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29209900
-
Androgen receptor transcriptionally regulates μ-opioid receptor expression in rat trigeminal ganglia.Neuroscience. 2016 Sep 7;331:52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.023. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 27320211 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse noxious inhibitory controls and brain networks are modulated in a testosterone-dependent manner in Sprague Dawley rats.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Sep 3;349:91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.04.055. Epub 2018 May 4. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29733874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal N, Pacher P, Tegeder I, Amaya F, Constantin CE, Brenner GJ, Rubino T, Michalski CW, Marsicano G, Monory K, Mackie K, Marian C, Batkai S, Parolaro D, Fischer MJ, Reeh P, Kunos G, Kress M, Lutz B, Woolf CJ, Kuner R. Cannabinoids mediate analgesia largely via peripheral type 1 cannabinoid receptors in nociceptors. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:870–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahluwalia J, Urban L, Capogna M, Bevan S, Nagy I. Cannabinoid 1 receptors are expressed in nociceptive primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience. 2000;100:685–8. - PubMed
-
- Amaya F, Shimosato G, Kawasaki Y, Hashimoto S, Tanaka Y, Ji RR, Tanaka M. Induction of CB1 cannabinoid receptor by inflammation in primary afferent neurons facilitates antihyperalgesic effect of peripheral CB1 agonist. PAIN®. 2006;124:175–83. - PubMed
-
- Ambalavanar R, Moutanni A, Dessem D. Inflammation of craniofacial muscle induces widespread mechanical allodynia. Neurosci Lett. 2006;399:249–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

